Ambroxol as a disease-modifying treatment to reduce the risk of cognitive impairment in GBA-associated Parkinson's disease: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial. The AMBITIOUS study protocol
- PMID: 38027469
- PMCID: PMC10679992
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjno-2023-000535
Ambroxol as a disease-modifying treatment to reduce the risk of cognitive impairment in GBA-associated Parkinson's disease: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial. The AMBITIOUS study protocol
Abstract
Background: Heterozygous mutations in the GBA gene, encoding the lysosomal enzyme β-glucocerebrosidase (GCase), are the most frequent genetic risk factor for Parkinson's disease (PD). GBA-related PD (GBA-PD) patients have higher risk of dementia and reduced survival than non-carriers. Preclinical studies and one open-label trial in humans demonstrated that the chaperone ambroxol (ABX) increases GCase levels and modulates α-synuclein levels in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
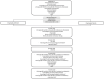
Methods and analysis: In this multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II clinical trial, we randomise patients with GBA-PD in a 1:1 ratio to either oral ABX 1.2 g/day or placebo. The duration of treatment is 52 weeks. Each participant is assessed at baseline and weeks 12, 26, 38, 52 and 78. Changes in the Montreal Cognitive Assessment score and the frequency of mild cognitive impairment and dementia between baseline and weeks 52 are the primary outcome measures. Secondary outcome measures include changes in validated scales/questionnaires assessing motor and non-motor symptoms. Neuroimaging features and CSF neurodegeneration markers are used as surrogate markers of disease progression. GCase activity, ABX and α-synuclein levels are also analysed in blood and CSF. A repeated-measures analysis of variance will be used for elaborating results. The primary analysis will be by intention to treat.
Ethics and dissemination: The study and protocols have been approved by the ethics committee of centres. The study is conducted according to good clinical practice and the Declaration of Helsinki. The trial findings will be published in peer-reviewed journals and presented at conferences.
Trial registration numbers: NCT05287503, EudraCT 2021-004565-13.
Keywords: CLINICAL NEUROLOGY; PARKINSON'S DISEASE; RANDOMISED TRIALS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RC has received speaking honoraria from Zambon Italia; Zambon SAU; Bial Italia Srl; advisory board fees from Bial; research support from the Italian Ministry of Health; he is Editor-in-Chief of the neuromuscular and movement disorders section of Brain Sciences (MDPI); Associate Editor of Parkinsonism and Related Disorders (Elsevier) and Frontiers in Ageing Neuroscience.
Figures