β-Cyclodextrin capped ZnS nanoparticles for CER-assisted colorimetric and spectrophotometric detection of Pb2⁺, Cu2⁺, and Hg2⁺ in an aqueous solution
- PMID: 38027943
- PMCID: PMC10663911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21850
β-Cyclodextrin capped ZnS nanoparticles for CER-assisted colorimetric and spectrophotometric detection of Pb2⁺, Cu2⁺, and Hg2⁺ in an aqueous solution
Abstract
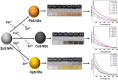
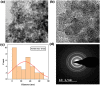
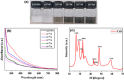
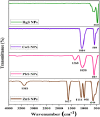
Herein, simple, low-cost, and room-temperature synthesis of beta-cyclodextrin (β-CD) stabilized zinc sulfide nanoparticle (ZnS NP) through the chemical precipitation method has been reported for cation exchange reaction (CER) based colorimetric sensing of Pb2+, Cu2+, and Hg2+. Formation of β-CD stabilized ZnS NPs (ZnS@β-CD) was verified by physicochemical characterization techniques such as XRD, XPS, FE-SEM, and TEM. ZnS@β-CD NPs showed color change selectively for the metal ions Pb2⁺, Cu2⁺, and Hg2⁺ among the various metal ions including Sn2⁺, Cr³⁺, Mn2⁺, Fe³⁺, Co2⁺, Ni2⁺, and Cd2⁺. The solubility product of reactants and the transformed products are the reason for selective CER of ZnS@β-CD NPs towards Pb2⁺, Cu2⁺, and Hg2⁺ ions. ZnS@β-CD NPs dispersion revealed rapid color change from white to orange, black, and bright yellow on the addition of higher concentrations of Pb2⁺, Cu2⁺, and Hg2⁺ respectively. This color change is due to the formation of complete CER-transformed nanostructures such as PbS, CuS, and HgS in higher concentrations (10⁻1- 10⁻³ M) of corresponding metal ions. The partial CER altered products Zn1-x,PbxS, Zn1-xCuxS and Zn1-xHgxS were detected due to the appearance of pale color in the lower metal ions concentrations of 10⁻⁴ - 10⁻⁶ M. This CER assisted transformation was also monitored through spectrophotometric methods. Moreover, infrared spectroscopic analysis was used to testify the structure of CER transformed product. The synthesized ZnS@β-CD NPs act as an efficient CER-based sensor for distinguishing and determining Pb2⁺, Cu2⁺, and Hg2⁺ at different level concentrations in the aqueous solution.
Keywords: Cation exchange reactions; Colorimetric sensor; Heavy metal ions; ZnS nanoparticles; β-Cyclodextrin.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures













References
-
- A.V.K K., Gangadharan D. Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects Adsorptive remediation of organic pollutant and arsenic (V) ions from water using Fe3O4 -MnO2 nanocomposite. Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects. 2022;29 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoso.2022.100837. - DOI
-
- Aoki K., Aschner M., Cullen J.T., Farkas E., Filella M., Hauser P., Klotz K., Küpper H., Maret W., Stewart T.J., Stillman M.J., Pecoraro V.L., Pohl H.R., Tylkowski B. Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG; 2017. Lead: its Effects on Environment and Health; p. 17. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

