Therapeutic effect of folic acid combined with decitabine on diabetic mice
- PMID: 38028519
- PMCID: PMC10626348
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2023.11.05
Therapeutic effect of folic acid combined with decitabine on diabetic mice
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the therapeutic effect of folic acid combined with decitabine on diabetic mice.
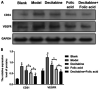
Methods: The diabetic model of db/db mice were randomly divided into model group, folic acid group, decitabine group, folic acid combined with decitabine group, and C57 mice as normal control group. The density of retinal blood vessels and retinal thickness were detected by fundus photography and optical coherence tomography, respectively. Pathological changes of retina were observed by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. The homocysteine (Hcy) in serum was detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). TdT-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) was used to detect apoptosis in retinal tissue. Evans blue dye was used to detect the permeability of retinal blood vessels. The platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) protein were detected by Western blot. The 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT) and 4-hydroxynonanine (4-HNE) were detected by immunohistochemistry.
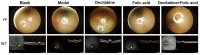
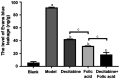
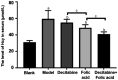
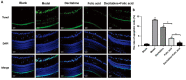
Results: The density of retinal blood vessels, retinal thickness, retinal vascular permeability and the proportion of apoptotic cells of retinal tissue in the model group increased significantly than control group (P<0.05). The Hcy in serum and the levels of CD31, VEGFR, 3-NT, and 4-HNE in retinal tissue increased significantly in the model group (P<0.01). Folic acid and decitabine both reversed these changes significantly, and the combination of the folic acid and decitabine worked best.
Conclusion: The combination of folic acid and decitabine has a more significant protective effect on the retina in diabetic mice.
Keywords: apoptosis; decitabine; diabetic model folic acid; mouse.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Protective Roles of Folic Acid in Preventing Diabetic Retinopathy Are Potentially Associated with Suppressions on Angiogenesis, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress.Ophthalmic Res. 2019;62(2):80-92. doi: 10.1159/000499020. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Ophthalmic Res. 2019. PMID: 31018207
-
Protective effects of a novel drug RC28-E blocking both VEGF and FGF2 on early diabetic rat retina.Int J Ophthalmol. 2018 Jun 18;11(6):935-944. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2018.06.07. eCollection 2018. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29977804 Free PMC article.
-
Compound Danshen dripping pills prevent early diabetic retinopathy: roles of vascular protection and neuroprotection.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1294620. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1294620. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38318138 Free PMC article.
-
Intravitreal injection of erythropoietin protects both retinal vascular and neuronal cells in early diabetes.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Feb;49(2):732-42. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0721. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18235022
-
Gypenoside XVII alleviates early diabetic retinopathy by regulating Müller cell apoptosis and autophagy in db/db mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 15;895:173893. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173893. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33493483
Cited by
-
Regulation role of miR-204 on SIRT1/VEGF in metabolic memory induced by high glucose in human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul 18;17(7):1232-1237. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.07.06. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39026923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai Y, Tu H, Wu C, Liu T, Chen S, Shen L, Xiao Q, Zhao S, Xu S, Lin W, Yan P, Dong J. Therapeutic potential of elema-1,3,7(11),8-tetraen-8,12-lactam from Curcuma wenyujin on diabetic retinopathy via anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;318(Pt A):116843. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
