Photocatalytic Hydrolysis-A Sustainable Option for the Chemical Upcycling of Polylactic Acid
- PMID: 38028741
- PMCID: PMC10655588
- DOI: 10.1021/acsenvironau.3c00040
Photocatalytic Hydrolysis-A Sustainable Option for the Chemical Upcycling of Polylactic Acid
Abstract
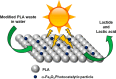
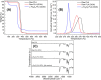
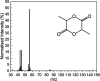
Plastic waste is a critical global issue, yet current strategies to avoid committing plastic waste to landfills include incineration, gasification, or pyrolysis high carbon emitting and energy consuming approaches. However, plastic waste can become a resource instead of a problem if high value products, such as fine chemicals and liquid fuel molecules, can be liberated from controlled its decomposition. This letter presents proof of concept on a low-cost, low energy approach to controlled decomposition of plastic, photocatalytic hydrolysis. This approach integrates photolysis and hydrolysis, both slow natural decomposition processes, with a photocatalytic process. The photocatalyst, α-Fe2O3, is embedded into a polylactic acid (PLA) plastic matrix. The photocatalyst/plastic composite is then immersed in water and subjected to low-energy (25 W) UV light for 90 h. The monomer lactide is produced as the major product. α-Fe2O3 (6.9 wt %) was found to accelerate the PLA degradation pathway, achieving 32% solid transformation into liquid phase products, in comparison to PLA on its own, which was found to not decompose, using the same conditions. This highlights a low energy route toward plastic waste upgrade and valorization that is less carbon intensive than pyrolysis and faster than natural degradation. By directly comparing a 25 W (0.025 kWh) UV bulb with a 13 kWh furnace, the photocatalytic reaction would directly consume 520× less energy than a conventional thermochemical pathway. Furthermore, this technology can be extended and applied to other plastics, and other photocatalysts can be used.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hundertmark T.; McNally M. M. C; Simons T. J.; Witte C.. How plastic waste could transform the chemical industry. McKinsey & Company, 2018. (accessed 15/10/22).
-
- Wang J.; Li X.; Zhang T.; Qian X.; Wang T.; Zhao Y. Rational design of photo- /electro-catalytic systems for the transformation of plastic wastes. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2023, 332, 122744.10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.122744. - DOI
-
- Li X.; Wang J.; Zhang T.; Yang S.; Sun M.; Qian X.; Wang T.; Zhao Y. Sustainable catalytic strategies for the transformation of plastic wastes into valued products. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 276, 118729.10.1016/j.ces.2023.118729. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

