Evaluation of diode laser efficacy in treating benign oral soft tissue masses: A case series
- PMID: 38029573
- PMCID: PMC10711152
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.109075
Evaluation of diode laser efficacy in treating benign oral soft tissue masses: A case series
Abstract
Introduction and importance: The diode laser, with a wavelength ranging from 810 to 980 nm, is a modern treatment modality that offers significant advantages in the management of benign oral soft tissue masses. Therefore, this report aimed to assess the efficacy of diode laser application for excisional biopsy of such masses.
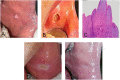
Case presentation: Three female patients, aged 9, 39, and 45 years, visited the Oral Medicine Clinic with complaints of painless masses in the oral cavity persisting for two to three months. Their intraoral examination showed the presence of pedunculated or sessile exophytic lesions with a smooth surface. The lesions appeared as single, pink to red protrusions located in various sites, including the left buccal mucosa, right lateral border of the tongue, and lower gingiva.
Clinical discussion: Excisional biopsy of the masses was carried out in the patients using the diode laser. The surgical procedures ranged from 10 to 20 min, with minimal intraoperative bleeding and precise cutting, while no pain was reported. Postoperatively, at two weeks and four months follow-up, the intraoral wounds exhibited excellent healing without complications such as pain, bleeding, swelling, scarring, infection, or mass recurrence. The clinical diagnosis of irritational fibroma (two cases) and fibrous epulis were confirmed by histopathological examination.
Conclusion: Diode laser emerges as a highly efficacious method for the excisional biopsy of benign oral soft tissue masses, providing intraoperative and postoperative advantages over scalpel surgery.
Keywords: Benign tumor; Biopsy; Diode laser; Excision; Oral mucosa.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Woods M., Reichart P.A. 2017. 87 - Surgical Management of Nonmalignant Lesions of the Mouth, P. A. Brennan, H. Schliephake, G. E. Ghali, and L. B. T.-M. S. Third E. Cascarini, Eds. Churchill Livingstone; pp. 1319–1334.
-
- Keche P.N., Gadpayle N.P., Gawarle S.H., Chamania G.A. An observational study of benign oral lesions in central India. Int. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017;3(4):816. doi: 10.18203/issn.2454-5929.ijohns20173201. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

