VEGFA mRNA-LNP promotes biliary epithelial cell-to-hepatocyte conversion in acute and chronic liver diseases and reverses steatosis and fibrosis
- PMID: 38029740
- PMCID: PMC10843608
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.10.008
VEGFA mRNA-LNP promotes biliary epithelial cell-to-hepatocyte conversion in acute and chronic liver diseases and reverses steatosis and fibrosis
Abstract
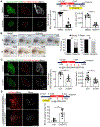
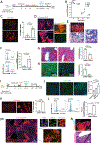
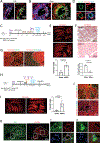
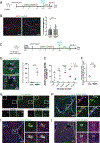
The liver is known for its remarkable regenerative ability through proliferation of hepatocytes. Yet, during chronic injury or severe hepatocyte death, proliferation of hepatocytes is exhausted. To overcome this hurdle, we propose vascular-endothelial-growth-factor A (VEGFA) as a therapeutic means to accelerate biliary epithelial-cell (BEC)-to-hepatocyte conversion. Investigation in zebrafish establishes that blocking VEGF receptors abrogates BEC-driven liver repair, while VEGFA overexpression promotes it. Delivery of VEGFA via nonintegrative and safe nucleoside-modified mRNA encapsulated into lipid nanoparticles (mRNA-LNPs) in acutely or chronically injured mouse livers induces robust BEC-to-hepatocyte conversion and elimination of steatosis and fibrosis. In human and murine diseased livers, we further identified VEGFA-receptor KDR-expressing BECs associated with KDR-expressing cell-derived hepatocytes. This work defines KDR-expressing cells, most likely being BECs, as facultative progenitors. This study reveals unexpected therapeutic benefits of VEGFA delivered via nucleoside-modified mRNA-LNP, whose safety is widely validated with COVID-19 vaccines, for harnessing BEC-driven repair to potentially treat liver diseases.
Keywords: BEC-derived intermediate liver progenitor cells; BEC-driven liver regeneration; KDR; VEGFA mRNA-LNP; acute liver injury; cholangiocyte-driven liver regeneration; chronic liver injury; ductular reaction; human liver cirrhosis; mouse liver injury model; zebrafish liver injury model.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests In accordance with the University of Pennsylvania’s policies and procedures and our ethical obligations as researchers, we report that D.W. is named on patents that describe the use of nucleoside-modified mRNA as a platform to deliver therapeutic proteins. D.W. and N.P. are also named on a patent describing the use of modified mRNA in lipid nanoparticles. D.W., N.P., and V.G.-E. are named on a patent describing the use of nucleoside-modified mRNA in lipid nanoparticles to treat liver diseases. D.W., R.D.-A., R.M.F., A.O., and A.S.-G. have a provisional international patent application that describes the use of nucleoside-modified mRNA in lipid nanoparticles to treat liver diseases. D.W., A.O., and A.S.-G. are co-founders and have a financial interest in Pittsburgh ReLiver, Inc.
Figures


Update of
-
VEGFA mRNA-LNP promotes biliary epithelial cell-to-hepatocyte conversion in acute and chronic liver diseases and reverses steatosis and fibrosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 18:2023.04.17.537186. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.17.537186. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell Stem Cell. 2023 Dec 7;30(12):1640-1657.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.10.008. PMID: 37131823 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 TR001810/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HL123828/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR001410/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK120531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK096990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 DK119973/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK117881/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 TR003289/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK127606/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101426/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK124361/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 TR002383/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI153064/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK119973/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK133404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099257/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 TR003289/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

