Physicochemical characterization and therapeutic potential of ink from squid, Sepioteuthis lessoniana
- PMID: 38031590
- PMCID: PMC10682348
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03830-6
Physicochemical characterization and therapeutic potential of ink from squid, Sepioteuthis lessoniana
Abstract
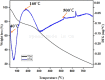
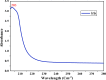
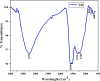
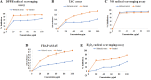
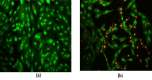
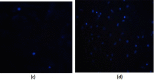
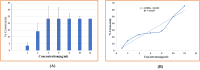
In the current study, the squid, Sepioteuthis lessoniana ink was used as a raw material. It summarizes physicochemical, elemental, and spectral properties (UV/Visible spectroscopy and FT-IR) of crude ink, whereas the biochemical analysis was performed with crude ink (CI) as well as melanin-free ink (MFI). The percentage yield was analyzed using various solvent extracts of CI and MFI. GC-MS was performed for the chemical constituents of the methanolic extract of ink. Furthermore, the methanolic extract was subjected to various biological applications. The physicochemical analysis defines the presence of moisture, ash, extractive value, solubility, and thermal stability of CI. The biochemical analysis reveals protein, lipid, and carbohydrate of 2.5, 2.2, and 2.37 mg/ml for CI and 2.8, 3.7, and 4.51 mg/ml for MFI respectively. The extract showed the highest zone of inhibition at 100 μg/ml. The antioxidant activity reveals the highest percentage of radical-scavenging activity in nitric oxide (NO) (89%), and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) assay showed the highest inhibition activity of 0.41 nm at 100 µg/ml. The cytotoxic ability of methanolic extract against MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line revealed an IC50 value of 10.13 μg/ml. Toxicity assay showed increased mortality of Artemia nauplii at higher concentrations (1000 ppm/40%) of extract. These findings indicate that S. lessoniana ink is a novel prospective product that needs to be characterized in order to increase its pharmacological activity.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13205-023-03830-6.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Antioxidant activity; Breast cancer cell line; GC; MS; Physicochemical analysis; Sepioteuthis lessoniana.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Abidin F, Sulmartiwi L, Saputra E (2021) Characteristics physicochemical of melanin from squid ink (loligo sp.) extracted by ethanol. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 679(1):012038. IOP Publishing
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

