The combination of baseline neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and dynamic changes during treatment can better predict the survival of osteosarcoma patients
- PMID: 38033504
- PMCID: PMC10682781
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1235158
The combination of baseline neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and dynamic changes during treatment can better predict the survival of osteosarcoma patients
Abstract
Background: Osteosarcoma is a primary malignant bone tumor with a high metastatic potential that accounts for a significant proportion of all bone tumors. The prognosis for patients with metastatic or recurrence disease remains poor. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has become a potential prognostic biomarker for cancer. Recent evidence suggests that the dynamic changes in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) during treatment may be more informative in predicting patient prognosis, but the value of dynamic NLR in osteosarcoma has not yet been determined.
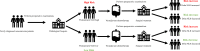
Methods: This retrospective study retrospectively analyzed the clinical information of 251 osteosarcoma patients diagnosed and treated in West China Hospital of Sichuan University, explored the impact of baseline NLR and changes in NLR during treatment on the prognosis of osteosarcoma patients, and further combined baseline NLR with Delta NLR to build an NLR staging system.
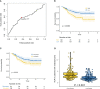
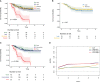
Results: The results showed that both baseline NLR and delta NLR had some predictive ability for the prognosis of osteosarcoma patients (P = 6.90e-4, P = 0.022). Patients with high baseline NLR were more likely to have a decrease in delta NLR (P = 1.24e-10). The NLR stage had a better predictive ability than baseline NLR and delta NLR, and was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival in osteosarcoma patients HR: 2.456 (1.625-3.710) (P = 1.97e-05).
Conclusion: NLR has value in continuous monitoring, and continuous monitoring of NLR can better predict the survival of osteosarcoma patients compared to baseline NLR.
Keywords: neutrophils-to-lymphocytes ratio; osteosarcoma; prognosis; risk model; survival.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Li, Lu, Wang, Li, Hu, He, Gong, Luo, Zhou, Min and Tu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prognostic performance of pre-treatment NLR and PLR in patients suffering from osteosarcoma.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Apr 29;14:127. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0889-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27125872 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic role of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, platelet/lymphocyte ratio, and lymphocyte/monocyte ratio in patients with osteosarcoma.Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2021;32(2):489-496. doi: 10.52312/jdrs.2021.79775. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2021. PMID: 34145828 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic change of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is predictive of pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer. 2020 Sep;27(5):982-988. doi: 10.1007/s12282-020-01096-x. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32306184
-
Systemic Inflammatory Markers for Predicting Overall Survival in Patients with Osteosarcoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Oct 21;2021:3456629. doi: 10.1155/2021/3456629. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34720749 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Urol. 2020 Jul 6;20(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-00665-8. BMC Urol. 2020. PMID: 32631294 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Prognostic Model Incorporating Relevant Peripheral Blood Inflammation Indicator to Predict Postherpetic Neuralgia in Patients with Acute Herpes Zoster.J Pain Res. 2024 Jul 1;17:2299-2309. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S466939. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38974827 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

