Rhizosphere microbial ecological characteristics of strawberry root rot
- PMID: 38033596
- PMCID: PMC10687216
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1286740
Rhizosphere microbial ecological characteristics of strawberry root rot
Abstract
Introduction: Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) holds a preeminent position among small fruits globally due to its delectable fruits and significant economic value. However, strawberry cultivation is hampered by various plant diseases, hindering the sustainable development of the strawberry industry. The occurrence of plant diseases is closely linked to imbalance in rhizosphere microbial community structure.
Methods: In the present study, a systematic analysis of the differences and correlations among non-culturable microorganisms, cultivable microbial communities, and soil nutrients in rhizosphere soil, root surface soil, and non-rhizosphere soil of healthy and diseased strawberry plants affected by root rot was conducted. The goal was to explore the relationship between strawberry root rot occurrence and rhizosphere microbial community structure.
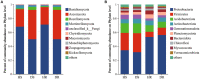
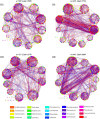
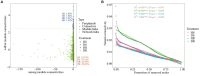
Results: According to the results, strawberry root rot altered microbial community diversity, influenced fungal community composition in strawberry roots, reduced microbial interaction network stability, and enriched more endophytic-phytopathogenic bacteria and saprophytic bacteria. In addition, the number of bacteria isolated from the root surface soil of diseased plants was significantly higher than that of healthy plants.
Discussion: In summary, the diseased strawberry plants changed microbial community diversity, fungal species composition, and enriched functional microorganisms significantly, in addition to reshaping the microbial co-occurrence network. The results provide a theoretical basis for revealing the microecological mechanism of strawberry root rot and the ecological prevention and control of strawberry root rot from a microbial ecology perspective.
Keywords: Fragaria × ananassa Duch.; culturable microorganisms; high-throughput sequencing; microbial network; root rot.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Kong, Fu, Shu, Xue, Lai and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Response of Yields, Soil Physiochemical Characteristics, and the Rhizosphere Microbiome to the Occurrence of Root Rot Caused by Fusarium solani in Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort.Microorganisms. 2024 Nov 18;12(11):2350. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12112350. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39597739 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Soil Microbial Communities between Healthy and Diseased Lycium barbarum cv. Ningqi-5 Plants with Root Rot.Microorganisms. 2023 Mar 8;11(3):694. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030694. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36985267 Free PMC article.
-
[Research on relationship between occurrence of root rot and changes of fungal communities in rhizosphere of Panax quinquefolius].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 May;43(10):2038-2047. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20180307.006. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29933668 Chinese.
-
Molecular characterization of microbial communities in the rhizosphere soils and roots of diseased and healthy Panax notoginseng.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2015 Nov;108(5):1059-74. doi: 10.1007/s10482-015-0560-x. Epub 2015 Aug 22. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2015. PMID: 26296378
-
High-Throughput Customization of Plant Microbiomes for Sustainable Agriculture.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Sep 8;11:569742. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.569742. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33013992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trichoderma harzianum prevents red kidney bean root rot by increasing plant antioxidant enzyme activity and regulating the rhizosphere microbial community.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 20;15:1348680. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1348680. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38572240 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Control of Root Rot of Strawberry by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Strains CMS5 and CMR12.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Jun 6;10(6):410. doi: 10.3390/jof10060410. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921396 Free PMC article.
-
Divergence of rhizosphere microbial communities between females and males of the dioecious Hippophae tibetana at different habitats.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 3;12(10):e0167024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01670-24. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39258920 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the SIX10 Gene in the Pathogenicity of Fusarium oxysporum Formae Speciales in Strawberries.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 28;26(3):1123. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031123. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940888 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Plant-Derived Biopesticide Mitigates Fusarium Root Rot of Angelica sinensis by Modulating the Rhizosphere Microbiome and Root Metabolome.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 6;13(16):2180. doi: 10.3390/plants13162180. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbas A., Mubeen M., Sohail M. A., Solanki M. K., Hussain B., Nosheen S., et al. . (2022). Root rot a silent alfalfa killer in China: distribution, fungal, and oomycete pathogens, impact of climatic factors and its management. Front. Microbiol. 13:961794. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.961794, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anandhakumar J., Zeller W. (2008). Biological control of red stele (Phytophthora fragariae var. fragariae) and crown rot (P. cactorum) disease of strawberry with rhizobacteria/Untersuchungen zur biologischen Bekämpfung der Roten Wurzelfäule und Rhizomfäule der Erdbeere (Phytophthora fragariae var. fragariae und F. cactorum) mit Rhizosphärebakterien. J. Plant Dis. Protect. 49–56.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

