Acupuncture for ventilator-dependent patients at a hospital-based respiratory care center: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 38033650
- PMCID: PMC10685379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imr.2023.100997
Acupuncture for ventilator-dependent patients at a hospital-based respiratory care center: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: In intensive care units, mechanical ventilation is an important therapy to help patients with dyspnea. However, long-term ventilator dependence would consume huge medical resources and increase the risk of morbidity and mortality. The aim of the study was to examine the efficacy of the acupuncture combined with western medical care on ventilator parameters in ventilator-dependent patients.
Methods: In this clinical trial, 80 ventilator-dependent patients aged 20 to 80 years old were randomly assigned to acupuncture group and control group in the respiratory care center (RCC) of Changhua Christian Hospital. Besides regular medical care and therapy, participants in the acupuncture group received acupuncture therapy at the same 17 acu-points for 20 minutes once a day, a total of 12 sessions. The ventilator parameters were recorded to evaluate the respiratory efficiency for all participants. The primary outcome was rapid shallow breathing index (RSBI), and secondary outcomes were respiratory rate (RR), tidal volume (TV) and ventilation per minute (MV).
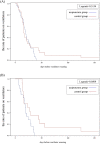
Results: Though there was no significant difference in the parameter between the acupuncture group and the control group, we found the trend of decreasing RSBI in the acupuncture group. In subgroup analyses, the mean of RSBI significantly decreased 16.02 (with the SD in 60.84) in acupuncture group, while it increased 17.84 (with the SD in 39.38) in control group (p=0.036) after 12 sessions.
Conclusion: Acupuncture treatment can improve breathing ability of patients with respirator dependence in respiratory care center.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Dyspnea; RSBI; Ventilator parameters; Ventilator-dependent.
© 2023 Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Acupuncture Treatment for Improving the Respiratory Status in Patients Receiving Prolonged Mechanical Ventilation in Intensive Care Units: A Retrospective Observational Study.J Altern Complement Med. 2018 Nov;24(11):1076-1084. doi: 10.1089/acm.2017.0365. Epub 2018 May 9. J Altern Complement Med. 2018. PMID: 29741919
-
The effect of flow trigger on rapid shallow breathing index measured through the ventilator.J Intensive Care Med. 2015 Feb;30(2):103-6. doi: 10.1177/0885066613504538. Epub 2013 Sep 24. J Intensive Care Med. 2015. PMID: 24067546
-
Comparative Assessment of the Effects of Two Methods of Pressure Support Adjustment on Respiratory Distress in Patients under Mechanical Ventilation Admitted to Intensive Care Units.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2021 Sep;25(9):1026-1030. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23960. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 34963721 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of rapid shallow breathing index displayed by the ventilator compared to the standard technique in patients with readiness for weaning.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Oct 2;21(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01680-7. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 34600522 Free PMC article.
-
Diaphragmatic ultrasonography-based rapid shallow breathing index for predicting weaning outcome during a pressure support ventilation spontaneous breathing trial.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Sep 7;22(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02133-5. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 36071420 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effect of acupuncture on reducing postoperative complications in fracture patients: A retrospective analysis using the TriNetX database.Bone Rep. 2025 Apr 4;25:101842. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2025.101842. eCollection 2025 Jun. Bone Rep. 2025. PMID: 40264751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burns S.M., Clochesy J.M., Hanneman S.K., Ingersoll G.E., Knebel A.R., Shekleton M.E. Weaning from long-term mechanical ventilation. Am J Crit Care. 1995;4(1):4–22. - PubMed
-
- Dries D.J. Weaning from mechanical ventilation. J Trauma. 1997;43(2):372–384. - PubMed
-
- Mancebo J. Weaning from mechanical ventilation. Eur Respir J. 1996;9(9):1923–1931. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

