Postoperative wound infection by nontuberculous mycobacteria; case series in Dhaka Medical College Hospital of Bangladesh
- PMID: 38033684
- PMCID: PMC10682233
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.8264
Postoperative wound infection by nontuberculous mycobacteria; case series in Dhaka Medical College Hospital of Bangladesh
Abstract
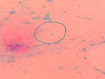
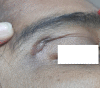
The incidence of nontuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) infections after operations is increasing in Bangladesh but data regarding clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis after treatment are lacking. In this case series, three patients having persistent serous discharge from incision wound after operation were studied. Discharge from wounds were collected, wet film microscopy was performed for pus cells and fungus, Gram stain, Ziehl-Neelsen (ZN) stain, culture in routine culture media and Lowenstein-Jensen (LJ) media, Xene-Xpert for mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for NTM were done. NTM-positive patients were treated initially for 6 weeks with four drugs regimen (clarithromycin 500 mg 12 hourly, ciprofloxacin 500 mg 12 hourly, linezolid 400 mg 12 hourly, and amikacin 500 mg 12 hourly), followed by 5 months with three drugs regimen (clarithromycin 500 mg 12 hourly, ciprofloxacin 500 mg 12 hourly, and linezolid 400 mg 12 hourly) as a maintenance dose. Cessation of discharge occurred within 3-4 weeks after starting treatment, and the wounds were healed.
Keywords: Bangladesh; Dhaka Medical College Hospital; acid‐fast bacilli (AFB); nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM); postoperative wound infection.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Vijayalaxmi B, Rani VU, Saraladevi R, Radhika L. Hospital outbreak of post caesarean wound infection with atypical mycobacteria. J Evol Med Dent Sci. 2016;5(52):3416‐3420.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

