Covalent targeting of non-cysteine residues in PI4KIIIβ
- PMID: 38033723
- PMCID: PMC10685791
- DOI: 10.1039/d3cb00142c
Covalent targeting of non-cysteine residues in PI4KIIIβ
Abstract
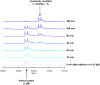
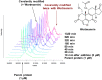
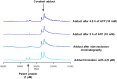
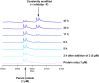
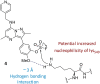
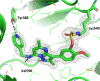
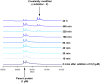
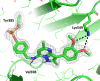
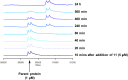
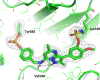
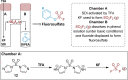
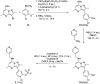
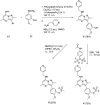
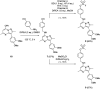
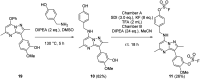
The synthesis and characterisation of fluorosulfate covalent inhibitors of the lipid kinase PI4KIIIβ is described. The conserved lysine residue located within the ATP binding site was targeted, and optimised compounds based upon reversible inhibitors with good activity and physicochemical profile showed strong reversible interactions and slow onset times for the covalent inhibition, resulting in an excellent selectivity profile for the lipid kinase target. X-Ray crystallography demonstrated a distal tyrosine residue could also be targeted using a fluorosulfate strategy. Combination of this knowledge showed that a dual covalent inhibitor could be developed which reveals potential in addressing the challenges associated with drug resistant mutations.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

