Cost-effectiveness of a decentralized, community-based "one-stop-shop" hepatitis C testing and treatment program in Yangon, Myanmar
- PMID: 38034058
- PMCID: PMC10684991
- DOI: 10.1002/jgh3.12978
Cost-effectiveness of a decentralized, community-based "one-stop-shop" hepatitis C testing and treatment program in Yangon, Myanmar
Abstract
Background and aim: The availability of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) treatment and point-of-care diagnostic testing has made hepatitis C (HCV) elimination possible even in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs); however, testing and treatment costs remain a barrier. We estimated the cost and cost-effectiveness of a decentralized community-based HCV testing and treatment program (CT2) in Myanmar.
Methods: Primary cost data included the costs of DAAs, investigations, medical supplies and other consumables, staff salaries, equipment, and overheads. A deterministic cohort-based Markov model was used to estimate the average cost of care, the overall quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gained, and the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of providing testing and DAA treatment compared with a modeled counterfactual scenario of no testing and no treatment.
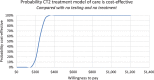
Results: From 30 January to 30 September 2019, 633 patients were enrolled, of whom 535 were HCV RNA-positive, 489 were treatment eligible, and 488 were treated. Lifetime discounted costs and QALYs of the cohort in the counterfactual no testing and no treatment scenario were estimated to be USD61790 (57 898-66 898) and 6309 (5682-6363) respectively, compared with USD123 248 (122 432-124 101) and 6518 (5894-6671) with the CT2 model of care, giving an ICER of USD294 (192-340) per QALY gained. This "one-stop-shop" model of care has a 90% likelihood of being cost-effective if benchmarked against a willingness to pay of US$300, which is 20% of Myanmar's GDP per capita (2020).
Conclusions: The CT2 model of HCV care is cost-effective in Myanmar and should be expanded to meet the National Hepatitis Control Program's 2030 target, alongside increasing the affordability and accessibility of services.
Keywords: Myanmar; cost‐effectiveness; direct‐acting antiviral treatment; hepatitis C; point‐of‐care testing.
© 2023 The Authors. JGH Open published by Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Foundation and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation . Hepatitis C . 2021. Available from URL: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c
-
- Lwin AA, Aye KS, Htun MM et al. Sero‐prevalence of hepatitis B and C Viral Infections in Myanmar: National and Regional Survey in 2015. Myanmar Health Sci. Res. J. 2017; 29: 167–175.
-
- World Health Organization . Global Health Sector Strategy on Viral Hepatitis 2016–2021. Towards Ending Viral Hepatitis. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016. Contract No.: WHO/HIV/2016.06.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources