Evaluation of proteolytic activity and serine proteases distribution in plasma from patients with bladder cancer
- PMID: 38034543
- PMCID: PMC10685322
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1276882
Evaluation of proteolytic activity and serine proteases distribution in plasma from patients with bladder cancer
Abstract
Background: Bladder cancer (BC) is an aggressive disease with a poor prognosis. A bladder tumor, like other malignant neoplasms, is characterized by the presence of both cancer cells and stromal cells which secrete cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and proteolytic enzymes. One such class of proteolytic enzymes are serine proteases, which take part in the tumor microenvironment formation via supporting and contributing to tumor progression. This study aims to evaluate the proteolytic activity and serine protease contribution in plasma from BC patients.
Methods: The research involved patients of Alexandrovsky city clinical hospital aged 52-76 with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. All examined patients were divided into five groups: the control group included conditionally healthy donors, while other patients were grouped according to their tumor stage (I, II, III and IV). Plasma plasminogen levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and the potential activity was measured by chromogenic plasminogen assay. Serine proteases fractions were obtained by the affinity chromatography method, and enzyme concentration in the selected fractions were determined by the Bradford method. Serine proteases distribution was investigated by electrophoresis in a polyacrylamide gel.
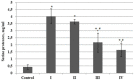
Results: It was determined that the concentration, potential activity of plasminogen, and the total amount of serine proteases in plasma from BC patients were greater than the values of the corresponding indicators in healthy donors. This could be one of the factors contributing to increased proteolysis seen in the process of carcinogenesis. Plasminogen concentration in BC patients with stage IV disease; however, displayed a tendency to be reduced compared to earlier stages, and the potential activity of plasminogen was significantly lower in patients with stages III - IV BC. Futhermore, a tumor stage specific gradual decline in the serine protease plasma content was shown. The results of electrophoretic analysis established a significant diminishment in the percentage of high molecular weight components (under non-reducing conditions) and their complete disappearance (under reducing conditions) in plasma serine protease fractions from BC patients. A decline in the percentage of heavy and light plasmin chains in BC patients was also observed. Additionally, a rise in the degraded forms of plasminogen/plasmin content was seen in BC samples, as well as the presence of fractions corresponding to trypsin and NE (under non-reducing conditions) that were absent in the control samples.
Conclusion: The results indicate significant changes in the proteolytic activity of plasma, from BC patients when compared to healthy controls, which is accompanied by alterations in serine protease distribution caused by tumor microenvironment pecularlities at the different stages of oncopathology.
Keywords: bladder cancer; elastase; electrophoresis; plasminogen; proteolysis; serine proteases.
Copyright © 2023 Synelnyk, Vovk, Halenova, Tytarenko, Raksha, Savchuk, Falalyeyeva, Ostapchenko, Yakovlev, Kozyk, Thorley and Strubchevska.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

