A web-based survey to map the electromyography practice in Brazil
- PMID: 38035579
- PMCID: PMC10689099
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1777007
A web-based survey to map the electromyography practice in Brazil
Abstract
Background: Detailed information about the electromyography practice in Brazil is largely unavailable.
Objective: To evaluate where and how electromyography is performed in Brazil, as well as regional disparities and the professional and academic credentials of electromyographers.
Methods: We conducted an internet-based survey of active Brazilian electromyographers. The websites of health insurance companies, professional academies, medical cooperatives, online search engines, and social networks in each Brazilian state were screened and we evaluated the credentials of each electromyographer listed in the Brazilian Federal Medical Board (BFMB) registration website and their online curricula vitae in the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, CNPq, in Portuguese). We also evaluated the same parameters in a control group of non-electromyographer neurologists randomly matched by geographical distribution and gender.
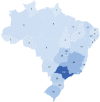
Results: We found 469 electromyographers (384 neurologists and 85 non-neurologists), with a male predominance. In total, 81.9% were BFMB-certified neurologists, 49.9%, BFMB-certified clinical neurophysiologists, and 10.4%, BFMB-certified physiatrists. Among the non-neurologists, 48.2% were physiatrists. Most electromyographers practiced in states on the Southern and Southeastern regions of Brazil. When adjusted by population, the Federal District and the states of Mato Grosso do Sul and Goiás presented the highest of eletromyographers density. Electromyographers were not more likely to have current/past academic affiliations.
Conclusion: In Brazil, electromyography is performed predominantly by neurologists, and half of them are BFMB-certified clinical neurophysiologists. The present study highlights regional disparities and may guide government-based initiatives, for instance, to improve the diagnosis of leprosy and the management of neuromuscular disorders within the Brazilian territory.
Antecedentes: Informações detalhadas sobre a prática de eletromiografia no Brasil são em grande parte indisponíveis.
Objetivo: Avaliar onde e como a eletromiografia é realizada no Brasil, as disparidades regionais, e as credenciais profissionais e acadêmicas dos eletromiografistas. MéTODOS: Realizamos uma enquete via internet de eletromiografistas brasileiros ativos. Foram rastreados sites de operadoras de planos de saúde, academias profissionais médicas, cooperativas médicas, ferramentas de busca online e redes sociais em cada estado brasileiro. Em seguida, avaliamos as credenciais de cada eletromiografista listado no site de registro do Conselho Federal de Medicina (CFM) e seus curricula vitae online no Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). Também avaliamos os mesmos parâmetros em um grupo controle de neurologistas não eletromiografistas pareados aleatoriamente por distribuição geográfica e gênero.
Resultados: Encontramos 469 eletromiografistas (384 neurologistas e 85 não neurologistas), com predominância do sexo masculino. Ao todo, 81,9% eram neurologistas com certificação confirmada pelo site do CFM, 49,9%, neurofisiologistas clínicos com certificação confirmada pelo site do CFM, e 10,4%, fisiatras com certificação confirmada pelo mesmo site. Entre os não neurologistas, 48,2% eram fisiatras. A maioria dos eletromiografistas atuava nos estados do Sul e do Sudeste. Quando ajustados pela população, o Distrito Federal e os estados de Mato Grosso do Sul e Goiás apresentaram a maior densidade de eletromiografistas. Os eletromiografistas não eram mais propensos a ter vínculos acadêmicos atuais/passados. CONCLUSãO: No Brasil, a eletromiografia é realizada predominantemente por neurologistas, e metade deles são neurofisiologistas clínicos com certificação confirmada pelo site do CFM. Este estudo destacou as disparidades regionais, e pode orientar ações governamentais para, por exemplo, melhorar o diagnóstico da hanseníase e o manejo das doenças neuromusculares no território brasileiro.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Deenen J C, Horlings C G, Verschuuren J J, Verbeek A L, van Engelen B G. The Epidemiology of Neuromuscular Disorders: A Comprehensive Overview of the Literature. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2015;2(01):73–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous