Development of postoperative delirium prediction models in patients undergoing cardiovascular surgery using machine learning algorithms
- PMID: 38036664
- PMCID: PMC10689441
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-48418-5
Development of postoperative delirium prediction models in patients undergoing cardiovascular surgery using machine learning algorithms
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Development of postoperative delirium prediction models in patients undergoing cardiovascular surgery using machine learning algorithms.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 22;14(1):4396. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51975-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38388546 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
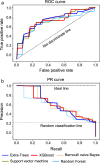
Associations between delirium and postoperative adverse events in cardiovascular surgery have been reported and the preoperative identification of high-risk patients of delirium is needed to implement focused interventions. We aimed to develop and validate machine learning models to predict post-cardiovascular surgery delirium. Patients aged ≥ 40 years who underwent cardiovascular surgery at a single hospital were prospectively enrolled. Preoperative and intraoperative factors were assessed. Each patient was evaluated for postoperative delirium 7 days after surgery. We developed machine learning models using the Bernoulli naive Bayes, Support vector machine, Random forest, Extra-trees, and XGBoost algorithms. Stratified fivefold cross-validation was performed for each developed model. Of the 87 patients, 24 (27.6%) developed postoperative delirium. Age, use of psychotropic drugs, cognitive function (Mini-Cog < 4), index of activities of daily living (Barthel Index < 100), history of stroke or cerebral hemorrhage, and eGFR (estimated glomerular filtration rate) < 60 were selected to develop delirium prediction models. The Extra-trees model had the best area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (0.76 [standard deviation 0.11]; sensitivity: 0.63; specificity: 0.78). XGBoost showed the highest sensitivity (AUROC, 0.75 [0.07]; sensitivity: 0.67; specificity: 0.79). Machine learning algorithms could predict post-cardiovascular delirium using preoperative data.Trial registration: UMIN-CTR (ID; UMIN000049390).
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder, 5th ed. Washington, DC (2013).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

