Tumor-suppressive functions of protein lysine methyltransferases
- PMID: 38036730
- PMCID: PMC10766653
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-023-01117-7
Tumor-suppressive functions of protein lysine methyltransferases
Abstract
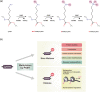
Protein lysine methyltransferases (PKMTs) play crucial roles in histone and nonhistone modifications, and their dysregulation has been linked to the development and progression of cancer. While the majority of studies have focused on the oncogenic functions of PKMTs, extensive evidence has indicated that these enzymes also play roles in tumor suppression by regulating the stability of p53 and β-catenin, promoting α-tubulin-mediated genomic stability, and regulating the transcription of oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Despite their contradictory roles in tumorigenesis, many PKMTs have been identified as potential therapeutic targets for cancer treatment. However, PKMT inhibitors may have unintended negative effects depending on the specific cancer type and target enzyme. Therefore, this review aims to comprehensively summarize the tumor-suppressive effects of PKMTs and to provide new insights into the development of anticancer drugs targeting PKMTs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Feinberg AP, Tycko B. The history of cancer epigenetics. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2004;4:143–153. - PubMed
-
- Ibrahim RK, Bruneau A, Bantignies B. Plant O-methyltransferases: molecular analysis, common signature and classification. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998;36:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Weisiger RA, Jakoby WB. Thiol S-methyltransferase. Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:257–262. - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. Histone methylation in transcriptional control. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002;12:198–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

