Improved green and red GRAB sensors for monitoring dopaminergic activity in vivo
- PMID: 38036855
- PMCID: PMC11009088
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-023-02100-w
Improved green and red GRAB sensors for monitoring dopaminergic activity in vivo
Abstract
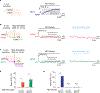
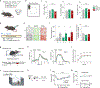
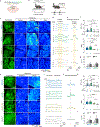
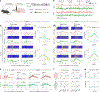
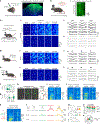
Dopamine (DA) plays multiple roles in a wide range of physiological and pathological processes via a large network of dopaminergic projections. To dissect the spatiotemporal dynamics of DA release in both dense and sparsely innervated brain regions, we developed a series of green and red fluorescent G-protein-coupled receptor activation-based DA (GRABDA) sensors using a variety of DA receptor subtypes. These sensors have high sensitivity, selectivity and signal-to-noise ratio with subsecond response kinetics and the ability to detect a wide range of DA concentrations. We then used these sensors in mice to measure both optogenetically evoked and behaviorally relevant DA release while measuring neurochemical signaling in the nucleus accumbens, amygdala and cortex. Using these sensors, we also detected spatially resolved heterogeneous cortical DA release in mice performing various behaviors. These next-generation GRABDA sensors provide a robust set of tools for imaging dopaminergic activity under a variety of physiological and pathological conditions.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
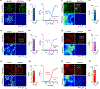


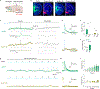
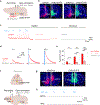
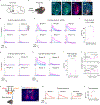
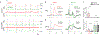
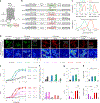
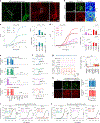
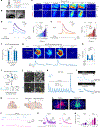
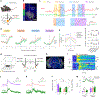
Update of
-
Improved dual-color GRAB sensors for monitoring dopaminergic activity in vivo.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 25:2023.08.24.554559. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.24.554559. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Methods. 2024 Apr;21(4):680-691. doi: 10.1038/s41592-023-02100-w. PMID: 37662187 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Björklund A. & Dunnett SB Dopamine neuron systems in the brain: an update. Trends Neurosci. 30, 194–202 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Klaus A, Alves da Silva J. & Costa RM What, if, and when to move: basal ganglia circuits and self-paced action initiation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci 42, 459–483 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Wise RA Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci 5, 483–494 (2004). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

