Leptin signaling in the dorsomedial hypothalamus couples breathing and metabolism in obesity
- PMID: 38039129
- PMCID: PMC10804286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113512
Leptin signaling in the dorsomedial hypothalamus couples breathing and metabolism in obesity
Abstract
Mismatch between CO2 production (Vco2) and respiration underlies the pathogenesis of obesity hypoventilation. Leptin-mediated CNS pathways stimulate both metabolism and breathing, but interactions between these functions remain elusive. We hypothesized that LEPRb+ neurons of the dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH) regulate metabolism and breathing in obesity. In diet-induced obese LeprbCre mice, chemogenetic activation of LEPRb+ DMH neurons increases minute ventilation (Ve) during sleep, the hypercapnic ventilatory response, Vco2, and Ve/Vco2, indicating that breathing is stimulated out of proportion to metabolism. The effects of chemogenetic activation are abolished by a serotonin blocker. Optogenetic stimulation of the LEPRb+ DMH neurons evokes excitatory postsynaptic currents in downstream serotonergic neurons of the dorsal raphe (DR). Administration of retrograde AAV harboring Cre-dependent caspase to the DR deletes LEPRb+ DMH neurons and abolishes metabolic and respiratory responses to leptin. These findings indicate that LEPRb+ DMH neurons match breathing to metabolism through serotonergic pathways to prevent obesity-induced hypoventilation.
Keywords: CP: Metabolism; CP: Neuroscience; designer receptor exclusively activated by designer drugs; dorsal raphe nucleus; hypercapnic ventilatory response; inspiratory flow limitation; intranasal administration; leptin receptor; obesity hypoventilation; obstructive sleep apnea; serotonin; sleep disordered breathing.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


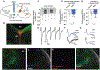
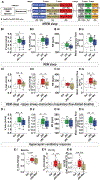

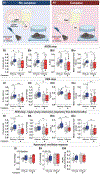

References
-
- Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, and Badr S (1993). The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N. Engl. J. Med 328, 1230–1235. - PubMed
-
- Tufik S, Santos-Silva R, Taddei JA, and Bittencourt LRA (2010). Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in the Sao Paulo Epidemiologic Sleep Study. Sleep Med. 11, 441–446. - PubMed
-
- Punjabi NM, Sorkin JD, Katzel LI, Goldberg AP, Schwartz AR, and Smith PL (2002). Sleep-disordered breathing and insulin resistance in middle-aged and overweight men. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 165, 677–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

