Cryogenic enrichment of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes from spiked whole blood
- PMID: 38040049
- PMCID: PMC10954416
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2023.104810
Cryogenic enrichment of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes from spiked whole blood
Abstract
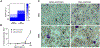
Each individual cell type typically requires a unique set of conditions for optimal cryopreservation outcome, which relates to its specific response to cryoprotective agent (CPA) toxicity, osmotic behavior and sensitivity to ice crystallization. Cryopreservation of heterogenous cell populations is therefore exceedingly difficult as it requires separate and often conflicting conditions for each cell type. Conversely, these contrasting conditions could be utilized to favor cryogenic preference of a single cell population within a heterogenous sample, leading to its enrichment by elimination of remaining cells. To establish proof-of-concept for this overall approach, a protocol was developed for the cryogenic enrichment of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes from whole blood. To accomplish this goal, we evaluated the effects of CPAs and cooling conditions during cryopreservation of whole blood samples spiked with P. falciparum gametocytes. We identified that cooling to -80 °C at a rate of -1 °C/min in the presence of 11 % glycerol selectively favors recovery of gametocytes. This protocol eliminates 95.3 ± 1.7 % of total blood cells and recovers 43.2 ± 6.5 % of parasites, leading to a 19-fold enrichment as assessed by microscopic examination of blood smears. This protocol is tunable, where gametocyte enrichment 900-fold may be feasible, however there is an apparent tradeoff in overall parasite recovery. Although translation of this protocol for point-of-care testing for malaria presents many challenges, the overall approach of cryogenic purification may prove useful for alternative diagnostic applications.
Keywords: Cryogenic; Enrichment; Gametocyte; Heterogenous sample; Plasmodium.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
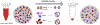
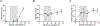
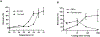

References
-
- Bottius E et al. Malaria: even more chronic in nature than previously thought; evidence for subpatent parasitaemia detectable by the polymerase chain reaction. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 90, 15–19 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

