Spatial transcriptomics deconvolution at single-cell resolution using Redeconve
- PMID: 38040768
- PMCID: PMC10692090
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43600-9
Spatial transcriptomics deconvolution at single-cell resolution using Redeconve
Abstract
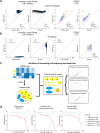
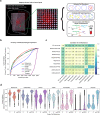
Computational deconvolution with single-cell RNA sequencing data as reference is pivotal to interpreting spatial transcriptomics data, but the current methods are limited to cell-type resolution. Here we present Redeconve, an algorithm to deconvolute spatial transcriptomics data at single-cell resolution, enabling interpretation of spatial transcriptomics data with thousands of nuanced cell states. We benchmark Redeconve with the state-of-the-art algorithms on diverse spatial transcriptomics platforms and datasets and demonstrate the superiority of Redeconve in terms of accuracy, resolution, robustness, and speed. Application to a human pancreatic cancer dataset reveals cancer-clone-specific T cell infiltration, and application to lymph node samples identifies differential cytotoxic T cells between IgA+ and IgG+ spots, providing novel insights into tumor immunology and the regulatory mechanisms underlying antibody class switch.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Janesick, A. et al. High resolution mapping of the breast cancer tumor microenvironment using integrated single cell, spatial and in situ analysis of FFPE tissue. bioRxiv, 2022.2010.2006.510405, 10.1101/2022.10.06.510405 (2022).
-
- He, S. et al. High-plex imaging of RNA and proteins at subcellular resolution in fixed tissue by spatial molecular imaging. Nat Biotechnol40, 1794–1806 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

