Influence of acute dietary nitrate supplementation timing on nitrate metabolism, central and peripheral blood pressure and exercise tolerance in young men
- PMID: 38040982
- PMCID: PMC11055761
- DOI: 10.1007/s00421-023-05369-z
Influence of acute dietary nitrate supplementation timing on nitrate metabolism, central and peripheral blood pressure and exercise tolerance in young men
Abstract
Purpose: Dietary nitrate (NO3-) supplementation can lower systolic blood pressure (SBP) and improve exercise performance. Salivary flow rate (SFR) and pH are key determinants of oral NO3- reduction and purported to peak in the afternoon. We tested the hypotheses that NO3--rich beetroot juice (BR) would increase plasma [nitrite] ([NO2-]), lower SBP and improve exercise performance to a greater extent in the afternoon (AFT) compared to the morning (MORN) and evening (EVE).
Method: Twelve males completed six experimental visits in a repeated-measures, crossover design. NO3--depleted beetroot juice (PL) or BR (~ 13 mmol NO3-) were ingested in the MORN, AFT and EVE. SFR and pH, salivary and plasma [NO3-] and [NO2-], brachial SBP and central SBP were measured pre and post supplementation. A severe-intensity exercise tolerance test was completed to determine cycling time to exhaustion (TTE).
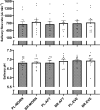
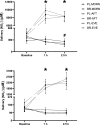
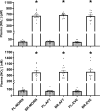
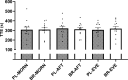
Results: There were no between-condition differences in mean SFR or salivary pH. The elevation in plasma [NO2-] after BR ingestion was not different between BR-MORN, BR-AFT and BR-EVE. Brachial SBP was unchanged following BR supplementation in all conditions. Central SBP was reduced in BR-MORN (- 3 ± 4 mmHg), BR-AFT (- 4 ± 3 mmHg), and BR-EVE (- 2 ± 3 mmHg), with no differences between timepoints. TTE was not different between BR and PL at any timepoint.
Conclusion: Acute BR supplementation was ineffective at improving TTE and brachial SBP and similarly effective at increasing plasma [NO2-] and lowering central SBP across the day, which may have implications for informing NO3- supplementation strategies.
Keywords: Beetroot juice; Cardiovascular health; Circadian rhythms; Exercise performance; Nitric oxide.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abu-Alghayth M, Vanhatalo A, Wylie LJ, McDonagh STJ, Thompson C, Kadach S, Kerr P, Smallwood MJ, Jones AM, Winyard PG. S-nitrosothiols, and other products of nitrate metabolism, are increased in multiple human blood compartments following ingestion of beetroot juice. Redox Biol. 2021;43:101974. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101974. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

