Association of MGMT and BIN1 genes with Alzheimer's disease risk across sex and APOE ε4 status
- PMID: 38041824
- PMCID: PMC10984453
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13550
Association of MGMT and BIN1 genes with Alzheimer's disease risk across sex and APOE ε4 status
Conflict of interest statement
Martin Ingelsson is a paid consultant to BioArtic.
Figures
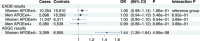
Comment on
-
Genome-wide association and multi-omics studies identify MGMT as a novel risk gene for Alzheimer's disease among women.Alzheimers Dement. 2023 Mar;19(3):896-908. doi: 10.1002/alz.12719. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Alzheimers Dement. 2023. PMID: 35770850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 3C Study Group . Vascular factors and risk of dementia: design of the Three‐City Study and baseline characteristics of the study population. Neuroepidemiology. 2003;22:316‐325. - PubMed
-
- Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, et al. Genome‐wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1094‐1099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

