The m6A reader ECT1 drives mRNA sequestration to dampen salicylic acid-dependent stress responses in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 38041863
- PMCID: PMC10896288
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koad300
The m6A reader ECT1 drives mRNA sequestration to dampen salicylic acid-dependent stress responses in Arabidopsis
Abstract
N 6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a common epitranscriptional mRNA modification in eukaryotes. Thirteen putative m6A readers, mostly annotated as EVOLUTIONARILY CONSERVED C-TERMINAL REGION (ECT) proteins, have been identified in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), but few have been characterized. Here, we show that the Arabidopsis m6A reader ECT1 modulates salicylic acid (SA)-mediated plant stress responses. ECT1 undergoes liquid-liquid phase separation in vitro, and its N-terminal prion-like domain is critical for forming in vivo cytosolic biomolecular condensates in response to SA or bacterial pathogens. Fluorescence-activated particle sorting coupled with quantitative PCR analyses unveiled that ECT1 sequesters SA-induced m6A modification-prone mRNAs through its conserved aromatic cage to facilitate their decay in cytosolic condensates, thereby dampening SA-mediated stress responses. Consistent with this finding, ECT1 overexpression promotes bacterial multiplication in plants. Collectively, our findings unequivocally link ECT1-associated cytosolic condensates to SA-dependent plant stress responses, advancing the current understanding of m6A readers and the SA signaling network.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
Figures

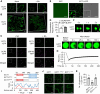
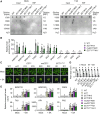
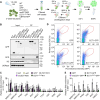
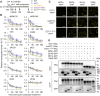

References
-
- Arribas-Hernandez L, Rennie S, Schon M, Porcelli C, Enugutti B, Andersson R, Nodine MD, Brodersen P. The YTHDF proteins ECT2 and ECT3 bind largely overlapping target sets and influence target mRNA abundance, not alternative polyadenylation. eLife 2021a:10:e72377. 10.7554/eLife.72377 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

