Protocol to characterize extracellular c-Src tyrosine kinase function through substrate interaction and phosphorylation
- PMID: 38043058
- PMCID: PMC10701435
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2023.102755
Protocol to characterize extracellular c-Src tyrosine kinase function through substrate interaction and phosphorylation
Abstract
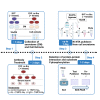
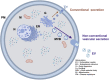
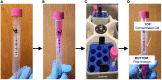
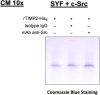
Cellular Src tyrosine kinase (c-Src) exists in the secretomes of several human cancers (extracellular, e-Src). Phosphoproteomics has demonstrated the existence of 114 potential extracellular e-Src substrates in addition to Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases 2. Here, we present a protocol to characterize secreted tyrosine-phosphorylated substrates as a result of c-Src expression and secretion. We describe steps for collecting cell secretomes and extracts, performing antibody treatment and Ni-NTA pull-down, and detecting protein-protein interaction and substrate Y-phosphorylation. This protocol is adaptable for studies examining the function of other extracellular kinases. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Backe et al. (2023)1 and Sánchez-Pozo et al. (2018).2.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell Biology; Molecular Biology.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Baker-Williams A.J., Hashmi F., Budzynski M.A., Woodford M.R., Gleicher S., Himanen S.V., Makedon A.M., Friedman D., Cortes S., Namek S., et al. Co-chaperones TIMP2 and AHA1 Competitively Regulate Extracellular HSP90:Client MMP2 Activity and Matrix Proteolysis. Cell Rep. 2019;28:1894–1906.e6. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

