Small-cell Lung Carcinoma with Gastrointestinal Pseudo-obstruction as a Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndrome Elicited by an Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor
- PMID: 38044152
- PMCID: PMC11309869
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2648-23
Small-cell Lung Carcinoma with Gastrointestinal Pseudo-obstruction as a Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndrome Elicited by an Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor
Abstract
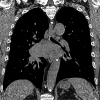
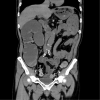
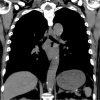
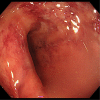
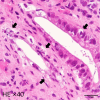
Gastrointestinal pseudo-obstruction (GIPO) is a phenotype of the paraneoplastic neurological syndrome (PNS). We herein report a case of small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) with GIPO elicited by an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI). A 75-year-old man with SCLC developed intractable intestinal obstruction after receiving one course of anticancer drugs (durvalumab, etoposide, and carboplatin). The serum anti-Hu antibody (Hu-Ab) was positive, and the patient was diagnosed with GIPO. Corticosteroid treatment did not improve the GIPO, and the patient died. There are few reports of GIPO after ICI treatment in patients with lung cancer, so a further investigation will be required to elucidate the mechanism by which ICIs elicit PNS. Checking for neuronal antibodies may help identify patients with SCLC who are at risk of developing PNS due to ICI treatment.
Keywords: anti-Hu antibody; gastrointestinal pseudo-obstruction; immune checkpoint inhibitor; paraneoplastic neurological syndrome; small-cell lung carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced anti-Hu antibody-associated gastrointestinal pseudo-obstruction: a case report and literature review.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 1;16:1555790. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1555790. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40236696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paraneoplastic Encephalitis and Enteric Neuropathy Associated With Anti-Hu Antibody in a Patient Following Immune-checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy.J Immunother. 2020 Jun;43(5):165-168. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000314. J Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32195750
-
[Anti-Hu syndrome - an unusual cause of vertigo].Praxis (Bern 1994). 2024 Nov;113(10):280-282. doi: 10.23785/PRAXIS.2024.10.008. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2024. PMID: 39665122 German.
-
Worsening of anti-Hu paraneoplastic neurological syndrome related to anti-PD-1 treatment: Case report and review of literature.J Neuroimmunol. 2020 Apr 15;341:577184. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2020.577184. Epub 2020 Feb 3. J Neuroimmunol. 2020. PMID: 32058173 Review.
-
Paraneoplastic myelitis associated with durvalumab treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2022 Feb;40(1):151-156. doi: 10.1007/s10637-021-01154-x. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Invest New Drugs. 2022. PMID: 34287773 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced anti-Hu antibody-associated gastrointestinal pseudo-obstruction: a case report and literature review.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 1;16:1555790. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1555790. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40236696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Commentary: Immune-related intestinal pseudo-obstruction caused by immune checkpoint inhibitors: case report.Front Oncol. 2025 May 23;15:1543608. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1543608. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40485737 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Antibody-positive paraneoplastic neurological syndromes associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review.J Neurol. 2025 Mar 5;272(3):249. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-12992-7. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40042691
References
-
- Benatar M, Blaes F, Johnston I, et al. . Presynaptic neuronal antigens expressed by a small cell lung carcinoma cell line. J Neuroimmunol 113: 153-162, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Matsuoka H, Kimura H, Koba H, et al. . Nivolumab-induced limbic encephalitis with anti-Hu antibody in a patient with advanced pleomorphic carcinoma of the lung. Clin Lung Cancer 19: e597-599, 2018. - PubMed

