COVID-19 Response of the Journal Public Health Reports (PHR), March 2020-March 2023
- PMID: 38044622
- PMCID: PMC10851904
- DOI: 10.1177/00333549231210514
COVID-19 Response of the Journal Public Health Reports (PHR), March 2020-March 2023
Abstract
Objective: Publication science is the scholarly study of various aspects of the academic publishing process. Its applications to COVID-19 literature have been limited. Here, we describe COVID-19 submissions to, and resulting articles published by, the journal Public Health Reports (PHR), an important resource for US public health practice.
Methods: We reviewed PHR's COVID-19 submissions and articles published between March 27, 2020, and March 27, 2023. We coded each article for article type, author affiliation, the categories listed in PHR's call for COVID-19 papers, and the public health emergency preparedness and response capabilities from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
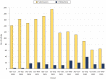
Results: During the study period, PHR received 1545 COVID-19 submissions and published 190 of those articles in a collection, COVID-19 Response. The COVID-19 Response collection included 102 research articles, 29 case study/practice articles, and 24 commentaries. The corresponding author of more than half (52.1%; n = 99) of the articles was affiliated with academia. By the categories listed in PHR's call for COVID-19 papers, 51 articles addressed health disparities, 38 addressed public health surveillance, and 34 addressed COVID-19 vaccination. By the CDC public health emergency preparedness and response capabilities, 87 articles addressed public health surveillance and epidemiologic investigation, 38 addressed community preparedness, and 32 addressed community recovery. The percentage of articles focused on policy/law was higher early in the pandemic (2020-2021) than later (2022-2023) (9.5% vs <3.0%). During the latter period, articles largely focused on vaccination (12.8%) and contact tracing (10.6%).
Conclusions: Articles published in PHR's COVID-19 Response collection covered a broad range of topics and were authored by contributors from diverse organizations. Our characterization of the COVID-19 output of a representative US public health practice journal can help academic publishing better address informational needs of public health responders.
Keywords: COVID-19; Public Health Reports; pandemic planning and response.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. The pandemic has triggered an unprecedented mobilisation of the scientific community. 2020. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://www.oecd.org/sti/science-technology-innovation-outlook/crisis-an...
-
- World Health Organization. Infodemic. 2023. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://www.who.int/health-topics/infodemic#tab=tab_1
-
- Kuzmichev A, Harada NM, Forbes CA, Dean HD. Public Health Reports in 2022: impact factor increase; COVID-19 coverage; authorship by state, tribal, local, and territorial agencies; and new department on public health ethics. Public Health Rep. 2023;138(4):578-585. doi:10.1177/00333549231168623 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Museum COVID-19 timeline. 2022. Last updated March 15, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/museum/timeline/covid19.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

