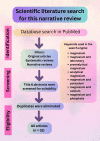
The Laboratory and Clinical Perspectives of Magnesium Imbalance
- PMID: 38045630
- PMCID: PMC10693313
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.49835
The Laboratory and Clinical Perspectives of Magnesium Imbalance
Abstract
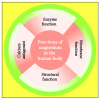
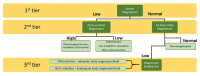
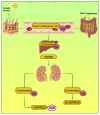
Magnesium (Mg2+) is a predominantly intracellular cation that plays significant roles in various enzymatic, membrane, and structural body functions. As a calcium (Ca2+) antagonist, it is imperative for numerous neuromuscular activities. The imbalance of body Mg2+ concentration leads to clinical manifestations ranging from asymptomatic to severe life-threatening complications. Therefore, the contribution of Mg2+ measurement regarding various laboratory and clinical aspects cannot be ignored. Mg2+ is often described as the forgotten analyte. However, its close relationship with body potassium (K+), Ca2+, and phosphate homeostasis proves that Mg2+ imbalance could co-exist as the root cause or the consequence of other electrolyte disorders. Meanwhile, several preanalytical, analytical, and postanalytical aspects could influence Mg2+ measurement. This review highlights Mg2+ measurement's laboratory and clinical issues and some analyte disturbances associated with its imbalance. Understanding this basis could aid clinicians and laboratory professionals in Mg2+ result interpretation and patient management.
Keywords: calcium; clinical standpoints; hypermagnesemia; hypomagnesemia; laboratory methodical aspects; magnesium disequilibrium; magnesium loading test; magnesium tolerance test; magnessium; post-analytical.
Copyright © 2023, Ab Rahim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Hypomagnesemia and hypermagnesemia. Van Laecke S. Acta Clin Belg. 2019;74:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Preanalytical quality improvement - an interdisciplinary journey, on behalf of the European Federation for Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (EFLM) Working Group for Preanalytical Phase (WG-PRE) Cadamuro J, Baird G, Baumann G, et al. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2022 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
