The Efficacy and Safety of Shashen-Maidong Decoction Combined with Western Medicine in the Treatment of Omicron Infected Individuals Over 85 Years Old: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 38045652
- PMCID: PMC10693277
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S433815
The Efficacy and Safety of Shashen-Maidong Decoction Combined with Western Medicine in the Treatment of Omicron Infected Individuals Over 85 Years Old: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Background: During the Omicron variant outbreak of COVID-19 (2022-2023), Chinese healthcare institutions combined traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) with Western medical practices to treat COVID-19 patients, especially the elderly. The efficacy and safety of this approach, especially for individuals aged over 85, need further investigation.
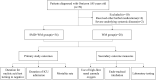
Methods: In this retrospective study, a cohort of 62 patients aged over 85 years, diagnosed with COVID-19 infection, was examined. Among them, 34 patients were administered Shashen-Maidong decoction in conjunction with Western medicine (SMD+WM group), while the remaining 28 patients received only Western medicine (WM group). Comparative analysis was conducted between the two groups, encompassing parameters such as the duration for the nucleic acid test to turn negative, length of intensive care unit (ICU) stay, mortality rate, utilization of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen (HFNC), occurrence of endo-tracheal intubation, frequency of recurrent respiratory infections within three months, and various laboratory indicators.
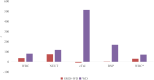
Results: There were no significant differences observed between the two groups in terms of the duration for the nucleic acid test to turn negative, the length of ICU stay, mortality rate, utilization of HFNC, performance of endo-tracheal intubation, or the frequency of recurrent respiratory infections within three months (P > 0.05). However, in comparison to the WM group, the SMD+WM group exhibited notably lower growth rates in white blood cell (WBC) and neutrophil (NEUT) values. Additionally, the SMD+WM group demonstrated superior improvement in cardiac troponin I (cTnI) and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) values.
Conclusion: In contrast to the administration of Western medicine alone, the combined use of Shashen-Maidong decoction with Western medicine significantly suppresses the increase in WBC count, particularly in NEUT levels, in elderly patients diagnosed with COVID-19. Moreover, this combined treatment exhibits a protective effect on cardiac function and demonstrates a relatively safe profile.
Keywords: COVID-19; Shashen-Maidong decoction; traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2023 Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shashen maidong decoction: the effect of TNF-α and IL-6 on lung cancer cachexia based on cancer toxicity theory.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Jun 15;13(6):6752-6758. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34306422 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Shashen Maidong Decoction in the Treatment of Pediatric Mycoplasma Pneumonia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 12;12:765656. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.765656. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34712144 Free PMC article.
-
Shashen-Maidong Decoction inhibited cancer growth under intermittent hypoxia conditions by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Dec 5;299:115654. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115654. Epub 2022 Sep 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36058477
-
Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Serum Cytokines for the Dampness-heat Syndrome of Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Altern Ther Health Med. 2023 Jul;29(5):386-395. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023. PMID: 37171947
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of High-Frequency Prescription of Zhigancao Decoction Combined with Conventional Western Medicine in the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Nov 9;2021:7140044. doi: 10.1155/2021/7140044. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34795787 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Peng Y, Guo Y, Zhang H, et al. Clinical characteristics and analysis of risk factors for disease progression of patients with SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant infection: a retrospective study of 25,207 cases in a Fangcang hospital. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:1009894. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.1009894 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials