Impact of amlodipine on clinical outcomes for heart failure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy: a Korean nationwide cohort study
- PMID: 38045912
- PMCID: PMC10690815
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1305824
Impact of amlodipine on clinical outcomes for heart failure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy: a Korean nationwide cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Amlodipine, widely used as a first-line treatment for hypertension, has inconclusive clinical evidence regarding its efficacy in patients with heart failure. This retrospective cohort study aimed to investigate the clinical effectiveness of amlodipine treatment after hospitalization for heart failure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCMP).
Methods: A total of 20,851 patients who were diagnosed with DCMP and admitted for heart failure between 2005 and 2016 according to Korean nationwide medical insurance service database were enrolled. Amlodipine use was defined as its prescription at the time of discharge and for at least 180 days within a year. The primary outcome was all-cause death, and the secondary outcome was heart failure rehospitalization during a 5-year period. The outcomes between patients who received amlodipine (n = 6,798) and those who did not (n = 14,053) were compared.
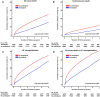
Results: During the 5-year follow-up, the group treated with amlodipine exhibited a significantly lower risk of all-cause death and heart failure rehospitalization than the group not treated with amlodipine [all-cause death: adjusted hazard ratio (HR): 0.64, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.59-0.70, p < 0.001; cardiovascular death: adjusted HR: 0.71, 95% CI: 0.62-0.81, p < 0.001; heart failure rehospitalization: adjusted HR: 0.92, 95% CI: 0.86-0.98, p = 0.006]. In a subgroup analysis, amlodipine had a significant impact on decreasing all-cause mortality in older adults, those with a higher systolic blood pressure, and those with a lower Charlson Comorbidity Index.
Conclusion: In summary, amlodipine use after hospitalization for heart failure in patients with DCMP was associated with a lower risk of all-cause death and readmission for heart failure.
Keywords: all-cause death; amlodipine; dilated cardiomyopathy; heart failure; hospitalization; hypertension; hypertension age; sex.
© 2023 Bae, Kim, You, Kim and Jung.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of amlodipine on the survival of patients with severe chronic heart failure due to a nonischemic cardiomyopathy: results of the PRAISE-2 study (prospective randomized amlodipine survival evaluation 2).JACC Heart Fail. 2013 Aug;1(4):308-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 Aug 5. JACC Heart Fail. 2013. PMID: 24621933 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of amlodipine on morbidity and mortality in severe chronic heart failure. Prospective Randomized Amlodipine Survival Evaluation Study Group.N Engl J Med. 1996 Oct 10;335(15):1107-14. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199610103351504. N Engl J Med. 1996. PMID: 8813041 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term β-blocker therapy and clinical outcomes after acute myocardial infarction in patients without heart failure: nationwide cohort study.Eur Heart J. 2020 Oct 1;41(37):3521-3529. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa376. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 32542362
-
Association of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist Use With All-Cause Mortality and Hospital Readmission in Older Adults With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Jun 5;2(6):e195892. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.5892. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31225889 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Cirrhosis and 30-Day Rehospitalization After Index Hospitalization for Heart Failure.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2022 Oct;47(10):100993. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2021.100993. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 34571101 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic enantioseparation system for racemate amlodipine based on a novel nanomaterial synthesized by chiral molecularly imprinted polymer and chiral metal-organic framework in capillary electrochromatography.Mikrochim Acta. 2025 Jun 28;192(7):463. doi: 10.1007/s00604-025-07242-6. Mikrochim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40580339
References
-
- Elkayam U, Amin J, Mehra A, Vasquez J, Weber L, Rahimtoola SH. A prospective, randomized, double-blind, crossover study to compare the efficacy and safety of chronic nifedipine therapy with that of isosorbide dinitrate and their combination in the treatment of chronic congestive heart failure. Circulation. (1990) 82(6):1954–61. 10.1161/01.cir.82.6.1954 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goldstein RE, Boccuzzi SJ, Cruess D, Nattel S. Diltiazem increases late-onset congestive heart failure in postinfarction patients with early reduction in ejection fraction. The adverse experience committee; and the multicenter diltiazem postinfarction research group. Circulation. (1991) 83(1):52–60. 10.1161/01.cir.83.1.52 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

