Successful pandemic management through computer science: a case study of a financial corporation with workers on premises
- PMID: 38045981
- PMCID: PMC10691253
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1208751
Successful pandemic management through computer science: a case study of a financial corporation with workers on premises
Abstract
Background: In November 2019, an infectious agent that caused a severe acute respiratory illness was first detected in China. Its rapid spread resulted in a global lockdown with negative economic impacts. In this regard, we expose the solutions proposed by a multinational financial institution that maintained their workers on premises, so this methodology can be applied to possible future health crisis.
Objectives: To ensure a secure workplace for the personnel on premises employing biomedical prevention measures and computational tools.
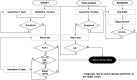
Methods: Professionals were subjected to recurrent COVID-19 diagnostic tests during the pandemic. The sanitary team implemented an individual following to all personnel and introduced the information in databases. The data collected were used for clustering algorithms, decision trees, and networking diagrams to predict outbreaks in the workplace. Individualized control panels assisted the decision-making process to increase, maintain, or relax restrictive measures.
Results: 55,789 diagnostic tests were performed. A positive correlation was observed between the cumulative incidence reported by Madrid's Ministry of Health and the headcount. No correlation was observed for occupational infections, representing 1.9% of the total positives. An overall 1.7% of the cases continued testing positive for COVID-19 after 14 days of quarantine.
Conclusion: Based on a combined approach of medical and computational science tools, we propose a management model that can be extended to other industries that can be applied to possible future health crises. This work shows that this model resulted in a safe workplace with a low probability of infection among workers during the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; epidemiology; health informatics; information management; occupational and industrial medicine.
Copyright © 2023 Partida-Hanon, Díaz-Garrido, Mendiguren-Santiago, Gómez-Paredes, Muñoz-Gutiérrrez, Miguel-Rodríguez and Reinoso-Barbero.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 5;10:CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 25;3:CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. PMID: 33502002 Updated.
-
International travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 25;3(3):CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33763851 Free PMC article.
-
Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID-19: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013574. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013574.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33959956 Free PMC article.
-
[Health professionals facing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: What are the mental health risks?].Encephale. 2020 Jun;46(3S):S73-S80. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2020.04.008. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Encephale. 2020. PMID: 32370984 Free PMC article. French.
-
Interventions to mitigate early spread of SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore: a modelling study.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Jun;20(6):678-688. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30162-6. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32213332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (2020). Listings of WHO’s response to COVID-19. Available at: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline (Accessed April 16, 2022).
-
- Ministerio de la Presidencia (2020). Relaciones con las Cortes y Memoria Democrática. Real Decreto 463/2020, de 14 de Marzo, Por El Que Se Declara El Estado de Alarma Para La Gestión de La Situación de Crisis Sanitaria Ocasionada Por El Covid-19. Available at: https://www.boe.es/boe/dias/2020/03/14/pdfs/BOE-A-2020-3692.pdf (Accessed October 19, 2023).
-
- Euronews (2020). Coronavirus: Half of humanity now on lockdown as 90 countries call for confinement. Available at: https://www.euronews.com/2020/04/02/coronavirus-in-europe-spain-s-death-... (Accessed December 9, 2022).
-
- Vicente-Herrero MT, Ramírez-Iñiguez de la Torre M, Capdevila L, Partida-Hanon A, Reinoso-Barbero L, López GA. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in spanish working population along the Covid-19 pandemic. Adiposity indicators and related variables. Acad J Health Sci Med Balear. (2022) 37:135–43. doi: 10.3306/ajhs.2022.37.02.132 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

