Milk exosomes anchored with hydrophilic and zwitterionic motifs enhance mucus permeability for applications in oral gene delivery
- PMID: 38047368
- PMCID: PMC10842862
- DOI: 10.1039/d3bm01089a
Milk exosomes anchored with hydrophilic and zwitterionic motifs enhance mucus permeability for applications in oral gene delivery
Abstract
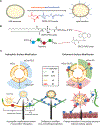
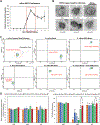
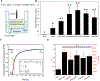
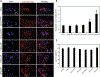
Exosomes have emerged as a promising tool for the delivery of drugs and genetic materials, owing to their biocompatibility and non-immunogenic nature. However, challenges persist in achieving successful oral delivery due to their susceptibility to degradation in the harsh gastrointestinal (GI) environment and impeded transport across the mucus-epithelium barrier. To overcome these challenges, we have developed high-purity bovine milk exosomes (mExo) as a scalable and efficient oral drug delivery system, which can be customized by incorporating hydrophilic and zwitterionic motifs on their surface. In our study, we observed significantly improved transport rates by 2.5-4.5-fold in native porcine intestinal mucus after the introduction of hydrophilic and zwitterionic surface modifications, as demonstrated by transwell setup and fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) analysis. Remarkably, mExo functionalized by a block peptide (BP), consisting of cationic and anionic amino acids arranged in blocks at the two ends, demonstrated superior tolerability in the acidic gastric environment (with a protein recovery rate of 84.8 ± 7.7%) and exhibited a 2.5-fold increase in uptake by intestinal epithelial cells. Furthermore, both mExo and mExo-BP demonstrated successful intracellular delivery of functional siRNA, resulting in up to 65% suppression of the target green fluorescence protein (GFP) gene expression at a low dose of siRNA (5 pmol) without causing significant toxicity. These findings highlight the immense potential of modifying mExo with hydrophilic and zwitterionic motifs for effective oral delivery of siRNA therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Milk exosomes with enhanced mucus penetrability for oral delivery of siRNA.Biomater Sci. 2021 Jun 15;9(12):4260-4277. doi: 10.1039/d0bm01497d. Biomater Sci. 2021. PMID: 33367332 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming multiple gastrointestinal barriers by bilayer modified hollow mesoporous silica nanocarriers.Acta Biomater. 2018 Jan;65:405-416. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.10.025. Epub 2017 Oct 14. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29037897
-
Milk Exosome-Liposome Hybrid Vesicles with Self-Adapting Surface Properties Overcome the Sequential Absorption Barriers for Oral Delivery of Peptides.ACS Nano. 2024 Aug 13;18(32):21091-21111. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c02560. Epub 2024 Aug 4. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39099105
-
Oral delivery of therapeutic peptides and proteins: Technology landscape of lipid-based nanocarriers.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Mar;182:114097. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.114097. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 34999121 Review.
-
Milk Exosomes: Next-Generation Agents for Delivery of Anticancer Drugs and Therapeutic Nucleic Acids.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 15;24(12):10194. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210194. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing exosomes for advanced osteoarthritis therapy.Nanoscale. 2024 Oct 24;16(41):19174-19191. doi: 10.1039/d4nr02792b. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 39323205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A game of hide-and-seek: how extracellular vesicles evade the immune system.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Aug;15(8):2624-2642. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01789-w. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39843837 Review.
-
Charge-Reversed Exosomes for Targeted Gene Delivery to Cartilage for Osteoarthritis Treatment.Small Methods. 2024 Sep;8(9):e2301443. doi: 10.1002/smtd.202301443. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Small Methods. 2024. PMID: 38607953
-
Intestinal nanoparticle delivery and cellular response: a review of the bidirectional nanoparticle-cell interplay in mucosa based on physiochemical properties.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Nov 1;22(1):669. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02930-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39487532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cationic-motif-modified exosomes for mRNA delivery to retinal photoreceptors.J Mater Chem B. 2024 Jul 31;12(30):7384-7400. doi: 10.1039/d4tb00849a. J Mater Chem B. 2024. PMID: 38946491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crater JS and Carrier RL, Macromol Biosci, 2010, 10, 1473–1483. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

