Exploring interactions between socioeconomic context and natural hazards on human population displacement
- PMID: 38049446
- PMCID: PMC10695951
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43809-8
Exploring interactions between socioeconomic context and natural hazards on human population displacement
Abstract
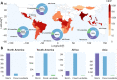
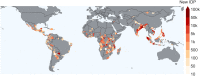
Climate change is leading to more extreme weather hazards, forcing human populations to be displaced. We employ explainable machine learning techniques to model and understand internal displacement flows and patterns from observational data alone. For this purpose, a large, harmonized, global database of disaster-induced movements in the presence of floods, storms, and landslides during 2016-2021 is presented. We account for environmental, societal, and economic factors to predict the number of displaced persons per event in the affected regions. Here we show that displacements can be primarily attributed to the combination of poor household conditions and intense precipitation, as revealed through the interpretation of the trained models using both Shapley values and causality-based methods. We hence provide empirical evidence that differential or uneven vulnerability exists and provide a means for its quantification, which could help advance evidence-based mitigation and adaptation planning efforts.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- McLeman R, Smit B. Migration as an adaptation to climate change. Clim. change. 2006;76:31–53. doi: 10.1007/s10584-005-9000-7. - DOI
-
- Internal Displacement Monitoring IDMC. Global Report on Internal Displacement.https://www.internal-displacement.org/global-report/grid2021/ (2021).
-
- Black R, et al. The effect of environmental change on human migration. Glob. Environ. change. 2011;21:S3–s11. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2011.10.001. - DOI
-
- McLeman R. Perception of climate migrants. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020;10:600–601. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-0803-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 101004188/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 101003469/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 951847/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 855187/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

