Estimating mortality of small passerine birds colliding with wind turbines
- PMID: 38049460
- PMCID: PMC10695956
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-46909-z
Estimating mortality of small passerine birds colliding with wind turbines
Abstract
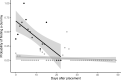
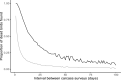
As demand for renewable energy is rising, wind power development is rapidly growing worldwide. In its wake, conflicts arise over land use changes converting pristine nature into industrial power plants and its associated adverse biodiversity effects, crowned by one of the most obvious and deadly consequences: bird collisions. Most post-construction studies report low levels of avian mortality, but the majority of these studies are conducted primarily on larger birds. However, the diversity and abundance of small passerine birds are rarely reflected in the carcass surveys, although they in numeric proportion to their abundances should be the most numerous. The assumption that surveys find all carcasses seems thus rarely fulfilled and passerine mortality is likely to be grossly underestimated. We therefore designed an experiment with dummy birds to estimate mortality of small-bodied passerines and other small-bodied birds during post-construction surveys, tested in a medium-sized wind farm in western Norway. The wind farm was surveyed weekly during the migration periods by carcass survey teams using trained dogs to find killed birds. The dogs in the carcass surveys were more successful in locating the large than the small dummy birds (60-200 g), where they found 74% of the large dummy birds. Detecting the smaller category (5-24 g) was more demanding and the dogs only found 17% of the small dummy birds. Correcting the post-construction carcass survey outcome with the results from the experiment leads to an almost fourfold increase in estimated mortality rates, largely due to the low detection rate of the smallest category. The detection rates will naturally vary between wind farms, depending on the specific habitat characteristics, the efficiency of the carcass surveys and the search intervals. Thus, implementing a simple experiment with dummy birds to future post-construction surveys will produce more accurate estimates of the wind turbine mortality rates, and thus improve our understanding of the biodiversity effects of conforming to a more sustainable future.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The post-construction study was financed by Guleslettene Wind Farm AS. The carcass survey teams partook by registering the dummy birds at the same time as they conducted the carcass surveys, but the experiment reported here was not required as part of the post-construction study by Norwegian authorities. Data handling and manuscript preparation was financed by the Norwegian Institute for Nature Research through the Research council of Norway (nr. 160022/F40).
Figures
References
-
- Poff NL, et al. The natural flow regime. Bioscience. 1997;47:769–784. doi: 10.2307/1313099. - DOI
-
- Lawrence, D. Klimaendring og framtidige flommer i Norge. Report No. NVE-Report 81 (2016).
-
- Rydell, J. et al. The effect of wind power on birds and bats. In A synthesis. Report 6511 (2012).
-
- Drewitt AL, Langston RH. Assessing the impacts of wind farms on birds. Ibis. 2006;148:29–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-919X.2006.00516.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

