First-line talazoparib with enzalutamide in HRR-deficient metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: the phase 3 TALAPRO-2 trial
- PMID: 38049622
- PMCID: PMC10803259
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-023-02704-x
First-line talazoparib with enzalutamide in HRR-deficient metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: the phase 3 TALAPRO-2 trial
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: First-line talazoparib with enzalutamide in HRR-deficient metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: the phase 3 TALAPRO-2 trial.Nat Med. 2024 May;30(5):1505. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-02835-9. Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 38297094 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
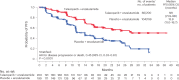
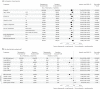
Preclinical evidence has suggested an interplay between the androgen receptor, which largely drives the growth of prostate cancer cells, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. This association provides a rationale for their co-inhibition for the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), an area of unmet medical need. The phase 3 TALAPRO-2 study investigated combining the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor talazoparib with enzalutamide versus enzalutamide alone as first-line treatment of mCRPC. Patients were prospectively assessed for tumor alterations in DNA damage response genes involved in homologous recombination repair (HRR). Two cohorts were enrolled sequentially: an all-comers cohort that was enrolled first (cohort 1; N = 805 (169 were HRR-deficient)), followed by an HRR-deficient-only cohort (cohort 2; N = 230). We present results from the alpha-controlled primary analysis for the combined HRR-deficient population (N = 399). Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to talazoparib or placebo, plus enzalutamide. The primary endpoint, radiographic progression-free survival, was met (median not reached at the time of the analysis for the talazoparib group versus 13.8 months for the placebo group; hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% confidence interval, 0.33 to 0.61; P < 0.0001). Data for overall survival, a key secondary endpoint, are immature but favor talazoparib (hazard ratio, 0.69; 95% confidence interval, 0.46 to 1.03; P = 0.07). Common adverse events in the talazoparib group were anemia, fatigue and neutropenia. Combining talazoparib with enzalutamide significantly improved radiographic progression-free survival in patients with mCRPC harboring HRR gene alterations, supporting talazoparib plus enzalutamide as a potential first-line treatment for these patients. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03395197 .
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.A.A. reports honoraria from Aculeus Therapeutics, Amgen, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Noxopharm, Pfizer, Sanofi, Telix Pharmaceuticals and Tolmar; consulting fees from Aculeus Therapeutics, Astellas Pharma, Janssen and Novartis; participation on advisory boards for Amgen, Arvinas, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Noxopharm, Pfizer, Sanofi, Telix and Tolmar; participation on a data safety monitoring board for OncoSec; research funding (institution unless stated otherwise) from Aptevo Therapeutics, Astellas Pharma (investigator), AstraZeneca (investigator), Bionomics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Hinova Pharmaceuticals, Ipsen, Janssen, Lilly, MedImmune, Merck Serono (investigator), MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi and Synthorx; and travel, accommodations and/or expenses from Amgen, Astellas Pharma, Janssen, Merck Serono, Novartis, Pfizer and Tolmar; and receiving medical writing services from Astellas Pharma, Exelixis and Pfizer; he is Chair of the Urologic Oncology Group for the Clinical Oncology Society of Australia, and Chair of the Translational Research Subcommittee and on the Scientific Advisory Committee for the ANZUP Cancer Trials Group. N.M. reports honoraria (personal) from Sanofi; research funding (institution) from Amgen, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Chugai Pharma, Eisai, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Pfizer, PRA Health Science, Roche, Seagen, Taiho and Takeda; and travel, accommodations and/or expenses (personal) from Pfizer. J.C. reports a consulting or advisory role for Advanced Accelerator Applications/Novartis, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, MSD Oncology, Pfizer, Roche and Sanofi; participation in speakers’ bureau for Astellas Pharma, Bayer and Johnson & Johnson; research funding (institution) from AB Science, Aragon Pharmaceuticals, AROG Pharmaceuticals, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca AB, AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Bayer AG, Blueprint Medicines, BN ImmunoTherapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim España SA, Bristol Myers Squibb International Corporation, Clovis Oncology, Cougar Biotechnology, Deciphera, Exelixis, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Incyte, Janssen-Cilag International NV, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Laboratoires Leurquin Mediolanum, Lilly, MedImmune, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Nanobiotix, Novartis Farmacéutica SA, Pfizer, Puma Biotechnology, Roche, Sanofi Aventis GmbH, SFJ Pharmaceuticals Group and Teva; and travel, accommodations and/or expenses from AstraZeneca, BMS, Ipsen and Roche. A.P.F. reports honoraria from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ipsen, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer and Roche; a consulting or advisory role for Bayer, Ipsen, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer and Roche; stock or stock options in Brazilian Information Oncology; and research funding from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, CAPES – CNPq, Foundation Medicine, Ipsen, MSD and Roche; and travel, accommodations and/or expenses from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, BMS, Ipsen, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer and Roche. U.D.G. reports a consulting or advisory role for Amgen, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dompé Farmaceutici, Eisai, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck KGaA, MSD, Novartis and Pfizer; research funding (institution) from AstraZeneca, Roche, and Sanofi; and travel, accommodations and/or expenses from AstraZeneca, Ipsen and Pfizer. J.Y.J. declares no competing interests. P.C.C.F. reports a consulting or advisory role for MSD and travel, accommodations and/or expenses from Pfizer. E.V. declares no competing interests. R.J.J. reports honoraria from Astellas Pharma, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck Serono, MSD, Pfizer and Roche; a consulting or advisory role for Astellas Pharma, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer and Roche; research funding from Astellas Pharma, Bayer, Clovis Oncology, Exelixis and Roche; and travel, accommodations and/or expenses from Bayer and Janssen. N.D.S. reports a consulting or advisory role for AbbVie, Alessa Therapeutics, Akido, Amgen, Arquer, Asieris, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boston Scientific, Bristol Myers Squibb, CG Oncology, Clarity Pharmaceuticals, Clovis Oncology, Dendreon, Exact Imaging, Exact Sciences, FerGene, Ferring, FIZE Medical, Foundation Medicine, GenesisCare, Genentech, Guardant Health, ImmunityBio, Incyte, Invitae, Janssen, Lantheus, Lilly, Mdxhealth, Merck, Minomic, Myovant Sciences, Myriad Genetics, Nymox, Pacific Edge Biotechnology, Pfizer, Photocure, PlatformQ, Profound, Promaxo, Propella Therapeutics, Protara, Sanofi, Sesen Bio, Speciality Networks, Telix Pharmaceuticals, Tolmar, UroGen Pharma, Vaxiion and Vessi; providing expert testimony for Ferring; and leadership or other fiduciary role in another board, society, committee, or advocacy group with Photocure. C.D. reports participation on advisory boards for Astellas Pharma, Bayer, Janssen and Pfizer; and research funding from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Dendreon, Hengrui Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Laekna Therapeutics, Myovant Sciences and Pfizer. S.Z. reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Amgen (personal and institution), Astellas (personal and institution), Bayer (personal and institution), Bristol Myers Squibb (personal and institution), Eisai (personal), Janssen (personal), Merck Serono (personal and institution), MSD (institution), Novartis (personal), and Pfizer (personal and institution); participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for Amgen (personal and institution), Bayer (personal and institution), Bristol Myers Squibb (institution), Eisai (personal), Gilead (personal), Ipsen (personal), Janssen (personal), Merck Serono (personal and institution), MSD (institution), Novartis (personal) and Pfizer (institution); research funding (institution) from Eisai; and travel, accommodations and/or expenses from Amgen, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck Serono, MSD and Pfizer. J.O. reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS Norway, Eisai, Ipsen, Janssen-Cilag, Merck and Roche; participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Eisai, Ipsen, Janssen-Cilag, Merck and Roche; and travel, accommodations and/or expenses from Astellas Pharma. D.Y. declares no competing interests. X.L., C.G.H., N.D.i.S., A.D.L. and F.Z. are employees of Pfizer and may hold Pfizer stock/stock options. N.A. has received an honorarium for consultancy before May 2021 from the following: Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, AVEO, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calithera Biosciences, Eisai, EMD Serono, Exelixis, Foundation Medicine, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Immunomedics, Janssen, Lilly and MEI Pharma; and research funding (institution) from Arvinas, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calithera Biosciences, Celldex, Clovis Oncology, CRISPR Therapeutics, Eisai, EMD Serono, Exelixis, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Immunomedics, Janssen, Lava, Lilly, Merck, Nektar, Neoleukin, Novartis, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Rexahn, Roche, Sanofi, Seagen, Takeda and TRACON. K.F. reports honoraria (institution) for participation in advisory boards and talks from Advanced Accelerator Applications/Novartis, Amgen, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Clovis Oncology, Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer and Sanofi; and honoraria (personal) for participation in advisory boards from Arvinas, CureVac, MacroGenics and Orion.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

