Dupilumab demonstrated efficacy and was well tolerated regardless of prior use of swallowed topical corticosteroids in adolescent and adult patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis: a subgroup analysis of the phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET study
- PMID: 38050037
- PMCID: PMC10894847
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330220
Dupilumab demonstrated efficacy and was well tolerated regardless of prior use of swallowed topical corticosteroids in adolescent and adult patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis: a subgroup analysis of the phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effect of long-term dupilumab on histological, symptomatic and endoscopic aspects of eosinophilic oesophagitis (EoE) in adolescent and adult patients with and without prior use of swallowed topical corticosteroids (STC) or prior inadequate response, intolerance or contraindication to STC.
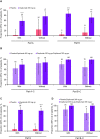
Design: Pre-specified analysis of data from the phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET study on patients who received dupilumab 300 mg once a week or placebo for 24 weeks (W24) in parts A and B, and an additional 28 weeks (W52) in part C. Patients were categorised as with/without prior STC use and with/without inadequate/intolerance/contraindication to STC. The proportion of patients achieving ≤6 eosinophils per high-power field (eos/hpf), absolute change in Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ) score, mean change in Endoscopic Reference Score and Histologic Scoring System grade/stage scores were assessed for each subgroup.
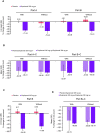
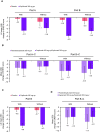
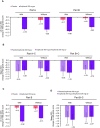
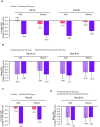
Results: Regardless of prior STC use, dupilumab increased the proportion of patients achieving ≤6 eos/hpf and improved DSQ score versus placebo at W24, with improvements maintained or improved at W52. The DSQ score and the proportion of patients achieving ≤6 eos/hpf after switching from placebo to dupilumab at W24 were similar to those observed in the dupilumab group at W24, regardless of prior STC use or inadequate/intolerance/contraindication to STC. Improvements in other outcomes with dupilumab were similar in patients with/without prior STC use or inadequate/intolerance/contraindication to STC.
Conclusion: Dupilumab 300 mg once a week demonstrated efficacy and was well tolerated in patients with EoE regardless of prior STC use or inadequate response, intolerance and/or contraindication to STC.
Trial registration number: NCT03633617.
Keywords: clinical trials; gastrointestinal pathology; health economics; inflammatory diseases; quality of life.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AJB: Dr Falk Pharma, Norgine, Nutricia, Sanofi, SST and Thelial—research funding; Alimentiv, Aqilion, AstraZeneca, Dr Falk Pharma, Laborie, Medtronic, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi—consulting fees. ED: Adare/Ellodi, Allakos, Arena/Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Receptos/BMS, GSK, Meritage, Miraca, Nutricia, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Revolo and Shire/Takeda—research funding; Abbott, AbbVie, Adare/Ellodi, Aimmune, Akesobio, Alfasigma, ALK, Allakos, Amgen, Aqilion, Arena/Pfizer, Aslan, AstraZeneca, Avir, Biorasi, Calypso, Celgene/Receptos/BMS, Celldex, Eli Lilly, EsoCap, Eupraxia, Ferring, Gossamer Bio, GSK, Holoclara, Invea, Knightpoint, Landos, LucidDx, Morphic, Nexstone Immunology, Nutricia, Parexel/Calyx, Phathom, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Revolo, Robarts/Alimentiv, Salix, Sanofi, Shire/Takeda, Target RWE and Upstream Bio—consulting fees; Allakos, Holoclara and Invea—educational funding. IH: Allakos, AstraZeneca, Calyx/Parexel, Eli Lilly, Ellodi/Adare, EsoCap, Gossamer Bio, Nexstone, Pfizer/Arena, Phathom, Receptos/BMS, Sanofi/Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and Shire/Takeda—consulting fees; Allakos, AstraZeneca, Ellodi/Adare, Pfizer/Arena, Receptos/BMS, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and Shire/Takeda—research funding; Sanofi/Regeneron Pharmaceuticals—speaker fees. AJL: Dr Falk Pharma and EsoCap—consulting fees; Dr Falk Pharma, Ellodi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals—research funding. CS: Adare Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Calypso, EsoCap, Dr Falk Pharma, GmbH and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals—consulting fees. AS, EM, JM and XS: employees of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and may hold stock and/or stock options in the company. EL, LG and LM: employees of Sanofi and may hold stock and/or stock options in the company.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
