Role of IFN-α in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 38051494
- PMCID: PMC10787895
- DOI: 10.1007/s11926-023-01125-6
Role of IFN-α in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Purpose of review: Type 1 interferons (IFN-I) are of increasing interest across a wide range of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Historically, research into their role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been relatively neglected, but recent work continues to highlight a potential contribution to RA pathophysiology.
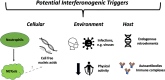
Recent findings: We emphasise the importance of disease stage when examining IFN-I in RA and provide an overview on how IFN-I may have a direct role on a variety of relevant cellular functions. We explore how clinical trajectory may be influenced by increased IFN-I signalling, and also, the limitations of scores composed of interferon response genes. Relevant environmental triggers and inheritable RA genetic risk relating to IFN-I signalling are explored with emphasis on intriguing data potentially linking IFN-I exposure, epigenetic changes, and disease relevant processes. Whilst these data cumulatively illustrate a likely role for IFN-I in RA, they also highlight the knowledge gaps, particularly in populations at risk for RA, and suggest directions for future research to both better understand IFN-I biology and inform targeted therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Early rheumatoid arthritis; Interferon gene signature; Rheumatoid arthritis; Type 1 interferons.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JDI discloses research grants from Pfizer, Janssen, and GSK; conference support from Eli Lilly and Gilead; speaker/consulting fees from AbbVie, BMS, Gilead, Roche, and UCB. FAHC discloses speaker fees from AstraZeneca. The remaining authors have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- •• Cooles FA, Isaacs JD. The interferon gene signature as a clinically relevant biomarker in autoimmune rheumatic disease. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021;4(1) 10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00254-X. A recent review exploring how a raised IGS can function as a clinically relevant biomarker in rheumatic diseases. - PubMed
-
- •• Rodriguez-Carrio J, Burska A, Conaghan PG, Dik WA, Biesen R, Eloranta ML, et al. EULAR points to consider for the measurement, reporting and application of IFN-I pathway activation assays in clinical research and practice. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(6):754–62. 10.1136/ard-2022-223628. A thorough review of using IFN-I assays in clinical research and their clinical utility. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

