Microglia Polarization and Antiglioma Effects Fostered by Dual Cell Membrane-Coated Doxorubicin-Loaded Hexagonal Boron Nitride Nanoflakes
- PMID: 38051559
- PMCID: PMC10739601
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.3c17097
Microglia Polarization and Antiglioma Effects Fostered by Dual Cell Membrane-Coated Doxorubicin-Loaded Hexagonal Boron Nitride Nanoflakes
Abstract
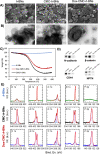
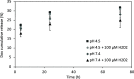
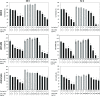
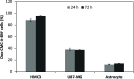
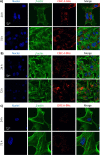
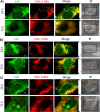
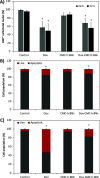
Microglial cells play a critical role in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) progression, which is considered a highly malignant brain cancer. The activation of microglia can either promote or inhibit GBM growth depending on the stage of the tumor development and on the microenvironment conditions. The current treatments for GBM have limited efficacy; therefore, there is an urgent need to develop novel and efficient strategies for drug delivery and targeting: in this context, a promising strategy consists of using nanoplatforms. This study investigates the microglial response and the therapeutic efficacy of dual-cell membrane-coated and doxorubicin-loaded hexagonal boron nitride nanoflakes tested on human microglia and GBM cells. Obtained results show promising therapeutic effects on glioma cells and an M2 microglia polarization, which refers to a specific phenotype or activation state that is associated with anti-inflammatory and tissue repair functions, highlighted through proteomic analysis.
Keywords: M2 polarization; doxorubicin; glioblastoma multiforme; hexagonal boron nitride nanoflakes; homotypic targeting; microglia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): FB is co-founder, Chief Scientific Officer and Board Member, VP is co-founder, Chief Executive Officer and President of the Board, AEDRC is Senior Scientists at BeDimensional S.p.A., a company commercializing 2D materials and that provided the h-BN nanoflakes tested in this work.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

