ACSS2 gene variants determine kidney disease risk by controlling de novo lipogenesis in kidney tubules
- PMID: 38051585
- PMCID: PMC10866669
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI172963
ACSS2 gene variants determine kidney disease risk by controlling de novo lipogenesis in kidney tubules
Abstract
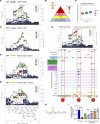
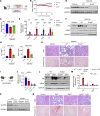
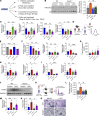
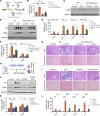
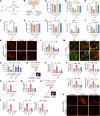
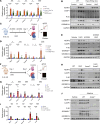
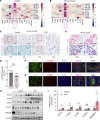
Worldwide, over 800 million people are affected by kidney disease, yet its pathogenesis remains elusive, hindering the development of novel therapeutics. In this study, we used kidney-specific expression of quantitative traits and single-nucleus open chromatin analysis to show that genetic variants linked to kidney dysfunction on chromosome 20 target the acyl-CoA synthetase short-chain family 2 (ACSS2). By generating ACSS2-KO mice, we demonstrated their protection from kidney fibrosis in multiple disease models. Our analysis of primary tubular cells revealed that ACSS2 regulated de novo lipogenesis (DNL), causing NADPH depletion and increasing ROS levels, ultimately leading to NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis. Additionally, we discovered that pharmacological inhibition or genetic ablation of fatty acid synthase safeguarded kidney cells against profibrotic gene expression and prevented kidney disease in mice. Lipid accumulation and the expression of genes related to DNL were elevated in the kidneys of patients with fibrosis. Our findings pinpoint ACSS2 as a critical kidney disease gene and reveal the role of DNL in kidney disease.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Fibrosis; Genetics; Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
- Targeting de novo lipogenesis to mitigate kidney disease doi: 10.1172/JCI178125
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK098656/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP3 DK108220/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM144613/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125497/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK087635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG074535/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK107397/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK125602/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK132630/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK123252/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076077/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK019525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK105821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK116005/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127979/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

