A Phase Ib Study of the DNA-PK Inhibitor Peposertib Combined with Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation in Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
- PMID: 38051750
- PMCID: PMC10870114
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1129
A Phase Ib Study of the DNA-PK Inhibitor Peposertib Combined with Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation in Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Peposertib-an orally administered DNA-dependent protein kinase inhibitor-has shown potent radiosensitization in preclinical models. This dose-escalation study (NCT03770689) aimed to define the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended phase II dose (RP2D) of peposertib plus capecitabine-based chemoradiotherapy (CRT) and assessed its safety and efficacy in locally advanced rectal cancer.
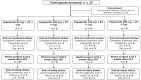
Patients and methods: Patients were treated for 5 to 5.5 weeks with 50- to 250-mg peposertib once daily, capecitabine 825 mg/m2 twice daily, and radiotherapy (RT), 5 days per week. Following clinical restaging (8 weeks after CRT completion), patients with clinical complete response (cCR) could opt for surveillance. Total mesorectal excision was recommended upon incomplete response (IR).
Results: Nineteen patients were treated with peposertib at doses of 50 mg (n = 1), 100 mg, 150 mg, and 250 mg (n = 6 each). Dose-limiting toxicities occurred in one out of five (100 mg), one out of six (150 mg), and three out of six (250 mg) evaluable patients. Peposertib ≤150 mg once daily was tolerable in combination with CRT. After 8 weeks of treatment with peposertib and CRT, the cCR was 15.8% (n = 3). Among the three patients with cCR, two underwent surgery and had residual tumors. Among the 16 patients with IR, seven underwent surgery and had residual tumors; five of the remaining nine patients opted for consolidative chemotherapy. The combined cCR/pathologic complete response (pCR) rate was 5.3% (n = 1, 100 mg cohort).
Conclusions: Peposertib did not improve complete response rates at tolerable dose levels. The study was closed without declaring the MTD/RP2D.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Comment in
-
DNA-dependent protein kinase inhibitor as a sensitizer of radiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Oct 31;15(5):2358-2362. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-373. Epub 2024 Oct 9. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39554583 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zenke FT, Zimmermann A, Sirrenberg C, Dahmen H, Kirkin V, Pehl U, et al. . Pharmacologic inhibitor of DNA-PK, M3814, potentiates radiotherapy and regresses human tumors in mouse models. Mol Cancer Ther 2020;19:1091–101. - PubMed
-
- Smith JJ, Chow OS, Gollub MJ, Nash GM, Temple LK, Weiser MR, et al. . Organ preservation in rectal adenocarcinoma: a phase II randomized controlled trial evaluating 3-year disease-free survival in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer treated with chemoradiation plus induction or consolidation chemotherapy, and total mesorectal excision or nonoperative management. BMC Cancer 2015;15:767. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

