Structural basis of nucleosomal H4K20 recognition and methylation by SUV420H1 methyltransferase
- PMID: 38052811
- PMCID: PMC10697951
- DOI: 10.1038/s41421-023-00620-5
Structural basis of nucleosomal H4K20 recognition and methylation by SUV420H1 methyltransferase
Abstract
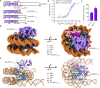
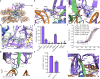
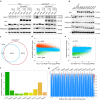
Histone lysine methyltransferase SUV420H1, which is responsible for site-specific di-/tri-methylation of histone H4 lysine 20 (H4K20), has crucial roles in DNA-templated processes, including DNA replication, DNA damage repair, and chromatin compaction. Its mutations frequently occur in human cancers. Nucleosomes containing the histone variant H2A.Z enhance the catalytic activities of SUV420H1 on H4K20 di-methylation deposition, regulating early replication origins. However, the molecular mechanism by which SUV420H1 specifically recognizes and deposits H4K20 methyl marks on nucleosomes remains poorly understood. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of SUV420H1 associated with H2A-containing nucleosome core particles (NCPs), and H2A.Z-containing NCPs. We find that SUV420H1 makes extensive site-specific contacts with histone and DNA regions. SUV420H1 C-terminal domain recognizes the H2A-H2B acidic patch of NCPs through its two arginine anchors, thus enabling H4K20 insertion for catalysis specifically. We also identify important residues increasing the catalytic activities of SUV420H1 bound to H2A.Z NCPs. In vitro and in vivo functional analyses reveal that multiple disease-associated mutations at the interfaces are essential for its catalytic activity and chromatin state regulation. Together, our study provides molecular insights into the nucleosome-based recognition and methylation mechanisms of SUV420H1, and a structural basis for understanding SUV420H1-related human disease.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
- 32200473/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32000423/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- RCYX20210706092045078/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
- 20220815154711001/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
- 20220817134430001/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

