Soluble CTLA-4 attenuates T cell activation and modulates anti-tumor immunity
- PMID: 38053333
- PMCID: PMC10861965
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.11.028
Soluble CTLA-4 attenuates T cell activation and modulates anti-tumor immunity
Abstract
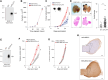
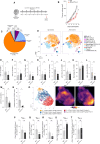
CTLA-4 is a crucial immune checkpoint receptor involved in the maintenance of immune homeostasis, tolerance, and tumor control. Antibodies targeting CTLA-4 have been promising treatments for numerous cancers, but the mechanistic basis of their anti-tumoral immune-boosting effects is poorly understood. Although the ctla4 gene also encodes an alternatively spliced soluble variant (sCTLA-4), preclinical/clinical evaluation of anti-CTLA-4-based immunotherapies have not considered the contribution of this isoform. Here, we explore the functional properties of sCTLA-4 and evaluate the efficacy of isoform-specific anti-sCTLA-4 antibody targeting in a murine cancer model. We show that expression of sCTLA-4 by tumor cells suppresses CD8+ T cells in vitro and accelerates growth and experimental metastasis of murine tumors in vivo. These effects were accompanied by modification of the immune infiltrate, notably restraining CD8+ T cells in a non-cytotoxic state. sCTLA-4 blockade with isoform-specific antibody reversed this restraint, enhancing intratumoral CD8+ T cell activation and cytolytic potential, correlating with therapeutic efficacy and tumor control. This previously unappreciated role of sCTLA-4 suggests that the biology and function of multi-gene products of immune checkpoint receptors need to be fully elucidated for improved mechanistic understanding of cancer immunotherapies.
Keywords: cancer; immune checkpoint; immune regulation; immunomodulation; immunotherapy; soluble CTLA-4.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests F.J.W. and L.N.D. are inventors on a patent (US8697845 B2) covering the use of the anti-sCTLA-4 monoclonal antibody as a therapeutic.
Figures



References
-
- Schneider H., Downey J., Smith A., Zinselmeyer B.H., Rush C., Brewer J.M., Wei B., Hogg N., Garside P., Rudd C.E. Reversal of the TCR stop signal by CTLA-4. Science. 2006;313:1972–1975. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

