Activity of pembrolizumab and lenvatinib in mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) endometrial cancer patients who have failed pembrolizumab monotherapy: A case series
- PMID: 38054201
- PMCID: PMC10694061
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gore.2023.101303
Activity of pembrolizumab and lenvatinib in mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) endometrial cancer patients who have failed pembrolizumab monotherapy: A case series
Abstract
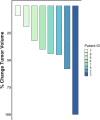
To evaluate the efficacy of the combination of pembrolizumab and lenvatinib in MMR deficient (dMMR) endometrial cancer (EC) patients who previously failed to respond to single-agent pembrolizumab. A retrospective review of MMR deficient endometrial cancer patients was performed. Patients who failed to respond to pembrolizumab as a single-agent and subsequently received a combination of pembrolizumab and lenvatinib were analyzed. RECIST 1.1 criteria was used to establish clinical response (complete response, partial response, stable disease, and progression) based on CT and/or PET, comparing imaging before and after the addition of lenvatinib. Radiologic review was conducted by an independent radiologist. Eight patients with dMMR EC meeting treatment criteria were identified. The patients' ages ranged from 54 to 80 and all tumors identified were of endometrioid histology. Initial pathologic stage ranged from FIGO stage IB to IVB and recurrence confirmed via imaging or tissue biopsy. Patients received a median of 14 cycles of therapy with pembrolizumab and lenvatinib (range 1-39). All patients had decrease in measurable disease with an objective response of 75 % (PR 62.5 %, CR 12.5 %). Both patients who received the initial recommended dose of 20 mg daily required a dose reduction. Based on this retrospective study, patients with dMMR EC without significant benefit from pembrolizumab monotherapy have a significant clinical response after the addition of lenvatinib. Combination therapy should be considered for dMMR EC patients who fail pembrolizumab monotherapy.
Keywords: Endometrial cancer; Lenvatinib; MMR deficient; Pembrolizumab.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, 2022. FDA grants regular approval to pembrolizumab and lenvatinib for advanced endometrial carcinoma [WWW Document]. FDA. URL https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grant... (accessed 9.26.23).
-
- Di Legge A., Trivellizzi I.N., Moruzzi M.C., Pesce A., Scambia G., Lorusso D. Phase 2 trial of nonpegylated doxorubicin (Myocet) as second-line treatment in advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011;21(8):1446–1451. - PubMed
-
- Kimura T., Kato Y.u., Ozawa Y., Kodama K., Ito J., Ichikawa K., Yamada K., Hori Y., Tabata K., Takase K., Matsui J., Funahashi Y., Nomoto K. Immunomodulatory activity of lenvatinib contributes to antitumor activity in the Hepa1-6 hepatocellular carcinoma model. Cancer Sci. 2018;109(12):3993–4002. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Makker V., Rasco D., Vogelzang N.J., Brose M.S., Cohn A.L., Mier J., Di Simone C., Hyman D.M., Stepan D.E., Dutcus C.E., Schmidt E.V., Guo M., Sachdev P., Shumaker R., Aghajanian C., Taylor M. Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced endometrial cancer: An interim analysis of a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(5):711–718. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials