Commonly asked questions about transcriptional activation domains
- PMID: 38056064
- PMCID: PMC11193542
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2023.102732
Commonly asked questions about transcriptional activation domains
Abstract
Eukaryotic transcription factors activate gene expression with their DNA-binding domains and activation domains. DNA-binding domains bind the genome by recognizing structurally related DNA sequences; they are structured, conserved, and predictable from protein sequences. Activation domains recruit chromatin modifiers, coactivator complexes, or basal transcriptional machinery via structurally diverse protein-protein interactions. Activation domains and DNA-binding domains have been called independent, modular units, but there are many departures from modularity, including interactions between these regions and overlap in function. Compared to DNA-binding domains, activation domains are poorly understood because they are poorly conserved, intrinsically disordered, and difficult to predict from protein sequences. This review, organized around commonly asked questions, describes recent progress that the field has made in understanding the sequence features that control activation domains and predicting them from sequence.
Keywords: Activation domain; Coactivator; Convolutional neural network; Intrinsically disordered protein; Protein function prediction; Protein-protein interactions (PPIs); RNA polymerase II; Transactivation domain; Transcription; Transcription factor; Transcriptional activation domain.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
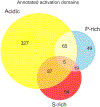
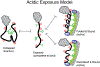
References
-
-
Soto LF, Li Z, Santoso CS, Berenson A, Ho I, Shen VX, Yuan S, Fuxman Bass JI: Compendium of human transcription factor effector domains. Molecular Cell 2022, 82:514–526.
After carefully curating a long list of published activation and repression domains, this paper analyzed conservation and genetic variation. DBDs are much more conserved than activation domains. Effector domains contain more neutral mutations and fewer clinical mutations than DBDs. An excellent starting point for people entering the field.
-
-
- Már M, Nitsenko K, Heidarsson PO: Multifunctional Intrinsically Disordered Regions in Transcription Factors. Chemistry 2023, - PubMed

