Inhibiting stromal Class I HDACs curbs pancreatic cancer progression
- PMID: 38057326
- PMCID: PMC10700526
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42178-6
Inhibiting stromal Class I HDACs curbs pancreatic cancer progression
Abstract
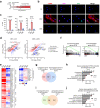
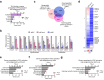
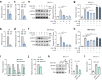
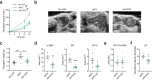
Oncogenic lesions in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) hijack the epigenetic machinery in stromal components to establish a desmoplastic and therapeutic resistant tumor microenvironment (TME). Here we identify Class I histone deacetylases (HDACs) as key epigenetic factors facilitating the induction of pro-desmoplastic and pro-tumorigenic transcriptional programs in pancreatic stromal fibroblasts. Mechanistically, HDAC-mediated changes in chromatin architecture enable the activation of pro-desmoplastic programs directed by serum response factor (SRF) and forkhead box M1 (FOXM1). HDACs also coordinate fibroblast pro-inflammatory programs inducing leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) expression, supporting paracrine pro-tumorigenic crosstalk. HDAC depletion in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and treatment with the HDAC inhibitor entinostat (Ent) in PDAC mouse models reduce stromal activation and curb tumor progression. Notably, HDAC inhibition (HDACi) enriches a lipogenic fibroblast subpopulation, a potential precursor for myofibroblasts in the PDAC stroma. Overall, our study reveals the stromal targeting potential of HDACi, highlighting the utility of this epigenetic modulating approach in PDAC therapeutics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.M.E. and M.D. are co-founders of a company developing entinostat. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Inhibiting Stromal Class I HDACs Curbs Pancreatic Cancer Progression.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 14:2023.09.12.557260. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.12.557260. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 6;14(1):7791. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42178-6. PMID: 37745372 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- BioProject/PRJNA524175
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

