Heterosynaptic plasticity-induced modulation of synapses
- PMID: 38057729
- PMCID: PMC10717068
- DOI: 10.1186/s12576-023-00893-1
Heterosynaptic plasticity-induced modulation of synapses
Abstract
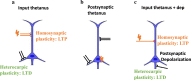
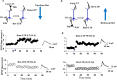
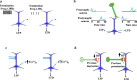
Plasticity is a common feature of synapses that is stated in different ways and occurs through several mechanisms. The regular action of the brain needs to be balanced in several neuronal and synaptic features, one of which is synaptic plasticity. The different homeostatic processes, including the balance between excitation/inhibition or homeostasis of synaptic weights at the single-neuron level, may obtain this. Homosynaptic Hebbian-type plasticity causes associative alterations of synapses. Both homosynaptic and heterosynaptic plasticity characterize the corresponding aspects of adjustable synapses, and both are essential for the regular action of neural systems and their plastic synapses.In this review, we will compare homo- and heterosynaptic plasticity and the main factors affecting the direction of plastic changes. This review paper will also discuss the diverse functions of the different kinds of heterosynaptic plasticity and their properties. We argue that a complementary system of heterosynaptic plasticity demonstrates an essential cellular constituent for homeostatic modulation of synaptic weights and neuronal activity.
Keywords: Dynamics; Heterosynaptic plasticity; Homosynaptic plasticity; Synaptic weight.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

