Biomechanical characteristics of a novel interspinous distraction fusion device in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a finite element analysis
- PMID: 38057738
- PMCID: PMC10701965
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-023-07066-6
Biomechanical characteristics of a novel interspinous distraction fusion device in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a finite element analysis
Abstract
Background: A novel interspinous distraction fusion (ISDF) device has been used to treat lumbar degenerative diseases. As a minimally invasive technique, ISDF differs from the traditional interspinous process distraction devices. Currently, biomechanical studies on ISDF are rare.
Objective: To investigate the biomechanical properties of the ISDF device (BacFuse) which is used to treat lumbar degenerative diseases.
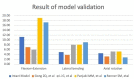
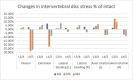
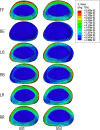
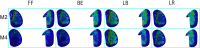
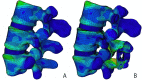
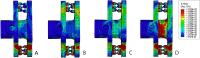
Methods: Three-dimensional L3-L5 models were created. The models were divided into four groups: intact (M1), local decompression alone (M2), internal fixation alone (M3) and local decompression combined with internal fixation (M4), based on different surgical procedures. Local laminectomy was performed to resect the lower part of the L4 lamina and the upper part of the L5 lamina at the right lamina of L4/5 in the M2 and M4 groups. After meshing the models elements, Abaqus were used to perform the finite element (FE) analysis. The intervertebral range of motion (ROM) was measured during flexion, extension, left lateral bending, right lateral bending, left rotation and right rotation under a follower load of 400 N with a 7.5Nm moment. The distributions of disc and facet joint stresses were observed and recorded. Spinal vertebral stress was compared, and internal fixation device stress was observed.
Results: The ROM of L4/5 in M2 increased in flexion, extension, left lateral bending, right lateral bending, left rotation and right rotation compared with that in M1. In all motion directions, the ROM at L4/5 decreased, and the ROM at L3/4 increased after implantation of the ISDF device in M3 and M4 groups. The disc stress and facet joint stresses in the instrumented segment decreased after implantation of the ISDF device. The spinous process loaded a certain amount of stress in M3 and M4 groups. The spikes of the internal fixation device were loaded with the maximum stress.
Conclusion: BacFuse exhibited a reduction in intervertebral ROM, as well as decreased stress on the intervertebral disc and facet joint, while also demonstrating a discernible impact on the upper adjacent segment.
Keywords: Biomechanical properties; Finite element analysis; Interspinous distraction fusion device; Lumbar degenerative diseases.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Schizas C, Pralong E, Tzioupis C, Kulik G. Interspinous distraction in lumbar spinal stenosis: a neurophysiological perspective. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013; 38(24): 2113–7 [PMID: 24026157 10.1097/01.brs.0000435031.96058.f6]. - PubMed
-
- Kaye AD, Edinoff AN, Temple SN, Kaye AJ, Chami AA, Shah RJ, Dixon BM, Alvarado MA, Cornett EM, Viswanath O, Urits I, Calodney AK. A Comprehensive Review of Novel Interventional techniques for Chronic Pain: spinal stenosis and degenerative disc Disease-MILD percutaneous image guided lumbar decompression, Vertiflex Interspinous Spacer, MinuteMan G3 Interspinous-Interlaminar Fusion. Adv Ther 2021; 38(9): 4628–45 [PMID: 34398386 DOI: 10.1007/s12325-021-01875-8]. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

