Ultrasound-guided dexmedetomidine combination with modified high fascia iliaca compartment block for arthroscopic knee surgery: what is the optimal dose of dexmedetomidine?
- PMID: 38057762
- PMCID: PMC10699007
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-023-02361-0
Ultrasound-guided dexmedetomidine combination with modified high fascia iliaca compartment block for arthroscopic knee surgery: what is the optimal dose of dexmedetomidine?
Erratum in
-
Correction: Ultrasound-guided dexmedetomidine combination with modified high fascia iliaca compartment block for arthroscopic knee surgery: what is the optimal dose of dexmedetomidine?BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Dec 22;23(1):421. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02391-8. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 38135886 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a common orthopedic procedure for end-stage knee osteoarthritis. Although effective in relieving pain and improving function, postoperative pain is still a common and distressing problem for many patients. This study aims to investigate efficacy of combined administration of dexmedetomidine and modified high fascia iliaca compartment block (H-FICB) in managing acute and chronic pain after TKA, as well as to identify the optimal dosage of dexmedetomidine.
Methods: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial was conducted to evaluate the effects of dexmedetomidine in patients undergoing TKA. A total of 96 patients undergoing TKA were randomly assigned to one of three groups, were treated with different doses of dexmedetomidine All groups received H-FIB. Pain scores, opioid consumption, side effects, and quality of life were recorded 48 h postoperatively.
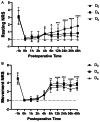
Results: The intraoperative consumption of remifentanil and propofol in Group Db was significantly reduced compared with that in Group D0 and Da (P < 0.05). Compared with D0 and Da group, Db group had the lowest number of rescue analgesia, analgesia time and morphine accumulative dosage 48 h after operation (P < 0.05). The Db group had the lowest scores on the numerical rating scale at rest (P < 0.05) and during movement (P < 0.01), followed by the Da group and then the D0 group. Additionally, the incidence of nausea and vomiting was significantly reduced in the Db group (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the Db group had the lowest incidence of chronic pain (P < 0.05).
Discussion: In comparison to the other two groups, the administration of combined dexmedetomidine and H-FIB resulted in a significant reduction in pain scores, opioid consumption, and side effects. The optimal dosage of dexmedetomidine was determined to be 1 μg/kg, which provided the most favorable pain relief with minimal adverse effects.
Keywords: Modified high fascia iliaca compartment block; Postoperative chronic pain; Total knee arthroplasty.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Li JF, Li H, Zhao H, Wang J, Liu S, Song Y, Wu HF. Combined use of intravenous and topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13018-017-0520-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akesen S, Akesen B, Atici T, Gurbet A, Ermutlu C, Ozyalcin A. Comparison of efficacy between the genicular nerve block and the popliteal artery and the capsule of the posterior knee (IPACK) block for total knee replacement Surgery: a prospective randomized controlled study. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2021;55(2):134–40. doi: 10.5152/j.aott.2021.20187. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boonmak P, Boonmak S. Epidural blood patching for preventing and treating post-dural puncture headache. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010(1):CD001791. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

