Single-cell histone chaperones patterns guide intercellular communication of tumor microenvironment that contribute to breast cancer metastases
- PMID: 38057779
- PMCID: PMC10702093
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-023-03166-4
Single-cell histone chaperones patterns guide intercellular communication of tumor microenvironment that contribute to breast cancer metastases
Abstract
Background: Histone chaperones (HCs) are crucial for governing genome stability and gene expression in multiple cancers. However, the functioning of HCs in the tumor microenvironment (TME) is still not clearly understood.
Methods: Self-tested single-cell RNA-seq data derived from 6 breast cancer (BC) patients with brain and liver metastases were reanalyzed by nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) algorithm for 36 HCs. TME subclusters were observed with BC and immunotherapy public cohorts to assess their prognosis and immune response. The biological effect of HSPA8, one of the HCs, was verified by transwell assay and wound-healing assays.
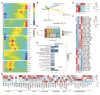
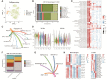
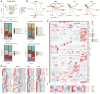
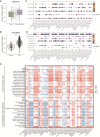
Results: Cells including fibroblasts, macrophages, B cells, and T cells, were classified into various subclusters based on marker genes. Additionally, it showed that HCs might be strongly associated with biological and clinical features of BC metastases, along with the pseudotime trajectory of each TME cell type. Besides, the results of bulk-seq analysis revealed that TME cell subclusters mediated by HCs distinguished significant prognostic value for BC patients and were relevant to patients' immunotherapy responses, especially for B cells and macrophages. In particular, CellChat analysis exhibited that HCs-related TME cell subclusters revealed extensive and diverse interactions with malignant cells. Finally, transwell and wound-healing assays exhibited that HSPA8 deficiency inhibited BC cell migration and invasion.
Conclusions: Collectively, our study first dissected HCs-guided intercellular communication of TME that contribute to BC metastases.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Histone chaperones; Prognosis; Single-cell; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

