Increased circulating FGF21 level predicts the burden of metabolic demands and risk of vascular diseases in adults with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 38057786
- PMCID: PMC10702049
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-023-01523-y
Increased circulating FGF21 level predicts the burden of metabolic demands and risk of vascular diseases in adults with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Objectives: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and metabolic stress, involved in the stepwise development of cardiovascular complications. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a novel hepatokine involved in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism, and has been linked to the prediction, treatment, and improvement of prognosis in multiple cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). The aim of this study is to explore the relationship between FGF21 levels and vascular diseases (VDs) including carotid atherosclerosis (CAS) and hypertension (HP) in patients with T2DM.
Methods: Baseline serum FGF21 was determined in a cross-sectional study of 701 patients with T2DM and 258 healthy control.
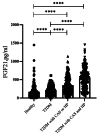
Results: The morbidity of CAS was increased in T2DM patients with HP as compared with those without (p < 0.001). The average serum FGF21 level of healthy was [123.9 (67.2-219.3)]. Baseline FGF21 was significantly higher in those who developed CAS or HP than in those who did not [305.9 (177.2-508.4) vs. 197.2 (129.7-308.3) pg/mL, p < 0.001]. In addition, an elevated serum FGF21 was observed in T2DM patients with HP and CAS than that of T2DM patients with CAS or HP [550.5 (312.6-711.3) vs. 305.9 pg/mL, p < 0.001]. Serum FGF21 levels were positively correlated with body mass index and carotid intima media thicknes (p < 0.05), the association remained significant after adjusting for age and T2DM duration. Furthermore, the multinomial logistic regression showed that serum FGF21 was independently associated with CAS and HP in patients with T2DM after adjustment for demographic and traditional VDs risk factors (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Baseline FGF21 is elevated in VDs during diabetes, changes of serum FGF21 levels were appropriately matched to metabolic stress. FGF21can be used as an independent predictor for diagnosing VDs and predicting prognosis.
Keywords: Carotid Atherosclerosis; Fibroblast growth factor 21; Hypertension; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; Vascular Diseases.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There were no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 is Related to Atherosclerosis Independent of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Predicts Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Events.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jun 2;9(11):e015226. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.015226. Epub 2020 May 20. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32431189 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 resistance is associated with body shape in patients with type 2 diabetes complicating hypertension.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jun 22;10:1168047. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1168047. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37424900 Free PMC article.
-
Serum fibroblast growth factor-21 levels are associated with carotid atherosclerosis independent of established cardiovascular risk factors.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Oct;33(10):2454-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301599. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23887638
-
The potential effect of metformin on fibroblast growth factor 21 in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Aug;31(4):1751-1760. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01255-4. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37337094 Review.
-
Role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in gestational diabetes mellitus: A mini-review.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019 Jan;90(1):47-55. doi: 10.1111/cen.13881. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 30346647 Review.
Cited by
-
Laparoscopic-guided transversus abdominis plane block combined with port-site infiltration for postoperative analgesia after gastric bypass: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial.Surg Endosc. 2025 Aug;39(8):4991-5000. doi: 10.1007/s00464-025-11870-7. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Surg Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40588600 Clinical Trial.
-
Establishment of a Direct Competitive ELISA for Camel FGF21 Detection.Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 14;12(2):170. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12020170. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40005931 Free PMC article.
-
FGF21 is a novel biomarker to predict fragility fractures in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 14;15(1):29848. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15104-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40813425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Samms RJ, Cheng CC, Fourcaudot M, Heikkinen S, Khattab A, Adams J, et al. FGF21 contributes to metabolic improvements elicited by combination therapy with exenatide and pioglitazone in patients with type 2 Diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2022;323(2):E123–32. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00050.2022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous